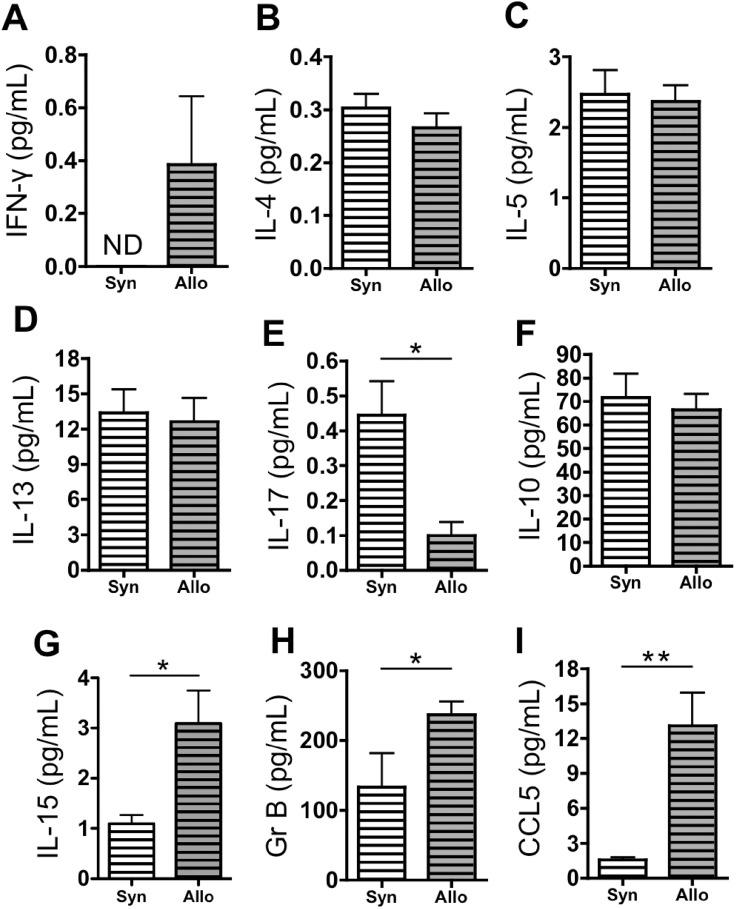
Figure 6. Allogeneic splenocyte transfer followed by inhaled LPS leads to an increase in pulmonary IFN-γ, granzyme B, and CCL5.
Rag1−/− mice received a transfer of allogeneic (Allo) or syngeneic (Syn) splenocytes followed by daily exposures to aerosolized LPS for 5 days starting 1 week after splenocyte transfer. Mice were euthanized 72 hours after the last LPS exposure and concentrations of proteins were measured in the BAL of AlloLPS and SynLPS mice using multiplex and ELISA assays. (A) IFN- γ is elevated in AlloLPS compared to SynLPS (p = ). (B–D) Th2 cytokines IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 are similar between AlloLPS and SynLPS. (E) IL-17 is reduced in AlloLPS compared to SynLPS (p = 0.0078). (F) IL-10 is unchanged between AlloLPS and SynLPS. (G) IL-15 is elevated in the BAL of AlloLPS compared to SynLPS (p = 0.014). (H) Granzyme B (Gr B) is elevated in the BAL of AlloLPS mice compared to SynLPS (p = 0.029). (I) CCL5 is elevated in the BAL of AlloLPS mice compared to SynLPS (p = 0.0023). Data represent the average +/− SEM and * = p<0.05 and ** = p<0.005. ND = non detectable. Data have been replicated in 2 independent experiments.