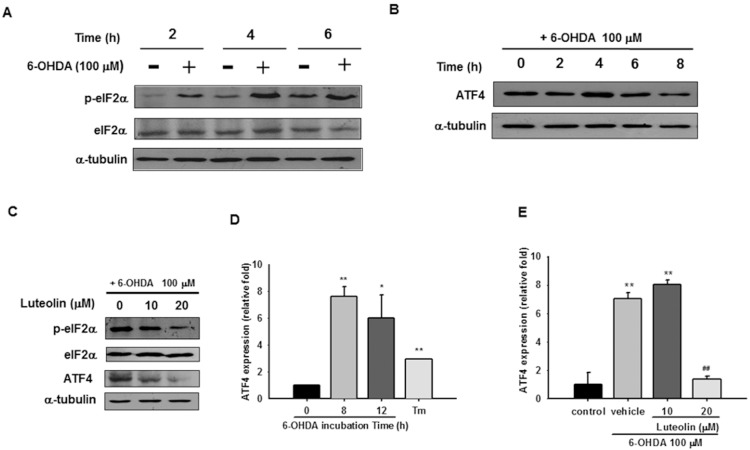
Figure 3. Effects of luteolin on 6-OHDA-mediated eIF2α-ATF4 activation.
(A) PC12 cells (1×106 cells/ml) were cultured in serum-free medium and then incubated with or without 6-OHDA (100 µM) for 2, 4, or 6 h. Cell lysates were prepared and immunoblotting was then carried out with antibodies against anti-p-eIF2α, anti-eIF2α and anti-α-tubulin. (B) PC12 cells were incubated with 6-OHDA (100 µM) for 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8 h. Cell lysates were prepared and immunoblotting was then carried out with antibodies against anti-ATF4 and anti-α-tubulin. (C) Cell lysates prepared from those co-treated with 6-OHDA (100 µM) and indicated concentration of luteolin for 4 h were subjected to p-eIF2α, eIF2α, ATF4, and α-tubulin analysis as described in Materials and Methods. These blots are representative ones from one of three independent experiments. (D) Changes in ATF4 mRNA expression after being incubated with 6-OHDA (100 µM) for 8 and 12 h. Cells treated with tunicamycin (Tm, 1 µg/ml) for 8 h served as a positive control. ATF4 mRNA expression was measured by RT-Q-PCR and normalized to β-actin, as described in the Materials and Methods. (E) Effect of luteolin on ATF4 mRNA expression. PC12 cells were treated with luteolin (10 or 20 µM) for 30 min before 6-OHDA (100 µM) insult for 8 h. RNA was then prepared for RT-Q-PCR analysis. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01 represent significant differences compared with the vehicle control (without 6-OHDA). ##, p<0.01 represents significant differences compared with the 6-OHDA-treated vehicle.