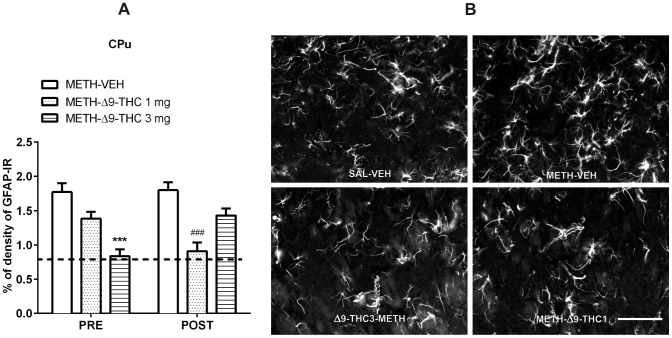
Figure 5. Δ9-THC reduces METH-induced astrogliosis in the CPu.
A. Rats were treated as described in the legend of Figure 4. Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of treatment (F(2,32) = 16.28, p<0.0001) as well as a significant interaction between time of treatment and treatment (F(2,32) = 8.12, p = 0.0014). Post-hoc comparisons showed that GFAP-IR was lower in the CPu of Post Δ9-THC (1 mg/kg) and Pre Δ9-THC (3 mg/kg) treated rats than in controls (METH-VEH). ***p<0.001 vs PRE METH-VEH and ### p<0.001 vs POST METH-VEH (Bonferroni's post-hoc test). Horizontal dot lines represent the values of percentage of GFAP-IR density (0.75±0.07) in SAL-VEH group. B. Representative images of GFAP immunostaining in the CPu 72 h after the last METH or SAL administration in SAL-VEH, METH-VEH, METH-Δ9-THC 1 and 3 mg. Scale bar = 100 µm.