Fig. 1.
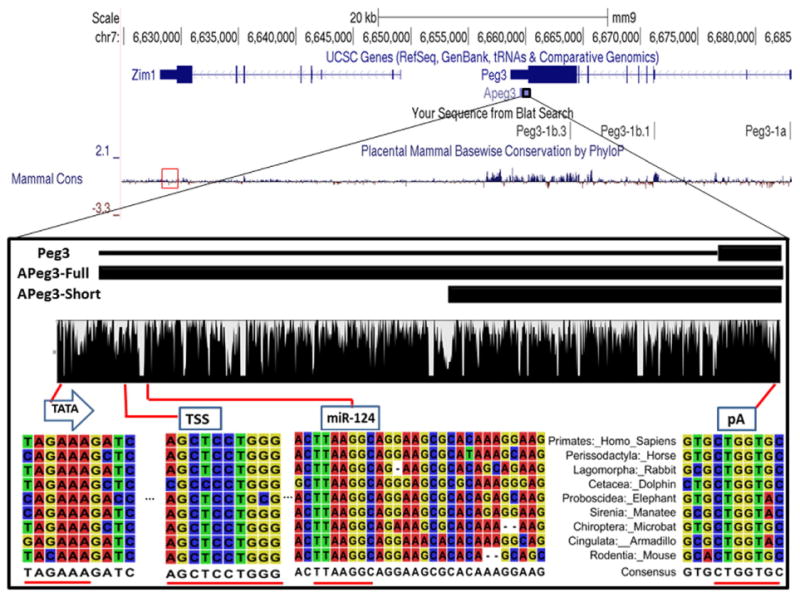
Evolutionary conservation of APeg3 among placental mammals. UCSC Genome Browser Mus musculus assembly 9 (mm9) displays the 100-kb genomic region surrounding mouse APeg3. The transcribed and exon regions of Peg3 and Zim1 are also presented along with the transcribed region of APeg3. Evolutionary conservation of this genomic interval among placental mammals is shown with a graphical output of the PhyloP analysis. PhyloP conservation analysis of Zim1 3′ UTR is designated in a red box. In a zoom-in view, two black boxes represent the different-length known cDNAs for APeg3. APeg3-Full is based on the deposited cDNA sequences from human and rat, while APeg3-Short is based on the cDNA sequences from mouse. The evolutionary conservation of APeg3 was further analyzed using the genomic sequences obtained from 9 representative placental mammals (Supplementary Fig. 1). This analysis identified a highly conserved TATA box (TATA), transcriptional start site (TSS) and a poly-adenylation signal (pA1). This analysis also confirmed the conservation of a potential target site for miRNA (miRNA-124). Areas of high conservation within these regions are underscored in red.
