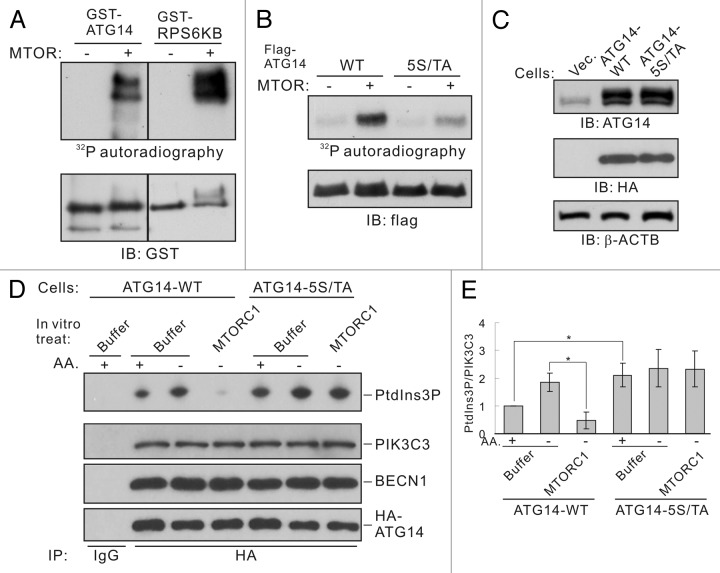
Figure 6. MTORC1 inhibits ATG14-PIK3C3 complex activity by phosphorylating ATG14. (A) Phosphorylation of ATG14 by MTOR. Recombinant GST-tagged ATG14 or RPS6KB were expressed and purified from E. coli, and used as substrates for in vitro MTOR kinase assay. Phosphorylation was determined by 32P-autoradiograph and the protein levels were determined by immunoblot. GST-RPS6KB was included as a positive control for MTOR kinase assay. (B) Mutation of the five phosphorylation residues abolishes ATG14 phosphorylation by MTOR in vitro. HEK293 cells were transfected with Flag-ATG14-WT or 5S/TA mutant as well as Myc-BECN1 and HA-PIK3C3. Flag-ATG14 proteins were purified by immunoprecipitation with Flag antibody and subjected to in vitro MTOR kinase assay. (C) HEK293 cells stably expressing HA-ATG14-WT or HA-ATG14-5S/TA. The HA-tagged ATG14 run slightly slower than the endogenous ATG14 (top panel). (D) Amino acid starvation activates ATG14-WT but not the ATG14-5S/TA associated PIK3C3 activity. ATG14-containing PIK3C3 complexes were immunoprecipitated from HEK293 stable cells under either nutrient-rich or -starvation conditions using HA antibody. The immune-complexes were treated with MTORC1 and then subjected to lipid kinase assay. (E) Quantification of (D). The error bars represent the standard error of the mean from independent experiments within same treatment group. Stars indicate a statistically significant difference.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.