Figure 2.
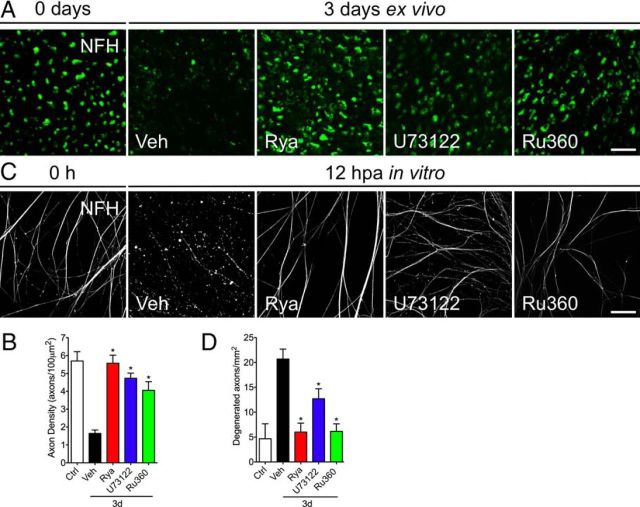
Pharmacological inhibition of ER calcium channels protects axotomy-induced axonal degeneration. Sciatic nerve explants from mice were incubated in vehicle (Veh) solution, Rya (50 μm), U73122 (20 μm), or Ru360 (50 μm) for 3 d and analyzed by immunofluorescence. A, Transverse sections of nerve explants stained for NFH. Axons in nerve explants incubated for 3 d with Rya, U73122, or Ru360 do not show signs of degeneration. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, Quantification of axons positive for NFH in explant cross-sections as shown in A, expressed as axons per 100 μm2. Statistically significant protection is seen after Rya, U73122, or Ru360 treatment at 3 d (*p < 0.05 by Student's t test compared with 3 d of vehicle; error bars indicate SEM). C, Embryonic DRG explants in vitro were axotomized and treated with Rya (5 μm), U73122 (2 μm), or Ru360 (5 μm). At 12 hpa, cultures were immunostained for NFH. Treatment with Rya, U73122, or Ru360 protects axons from axotomy-induced degeneration. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Quantification of axonal preservation by the degeneration index (area neurites fragmented/total area; for details, see Materials and Methods). Rya, U73122, or Ru360 protects injury-induced neurite degeneration at 12 hpa (n = 9, 3 images per sample, 3 samples per condition, 3 repetitions; *p < 0.05 by Student's t test compared with control; error bars indicate SEM).