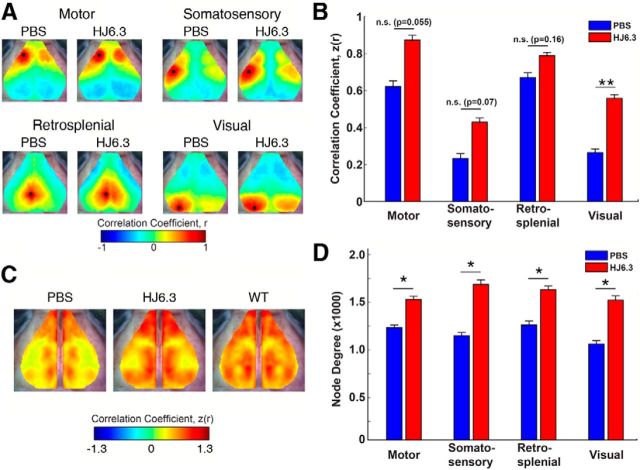
Figure 7.
HJ6.3 treatment improved brain functional connectivity assessed by fcOIS. Seven-month-old female APP/PS1 mice received 10 mg/kg weekly intraperitoneal injections of HJ6.3 or PBS for 21 weeks. At the age of 12 months, fcOIS was performed to assess the resting state functional connectivity of the brain before euthanizing the mice. A, Composite, group-averaged, functional correlation maps of motor, somatosensory, retrosplenial, and visual cortices in HJ6.3-treated (n = 15) and PBS-treated (n = 14) APP/PS1 mice. Black circles denote seed position. B, Regional bilateral functional correlation of PBS-treated (blue) and HJ6.3-treated (red) APP/PS1 mice. C, Consensus bilateral functional connectivity maps generated for HJ6.3 and PBS treated APP/PS1 mice and age-matched untreated wild-type B6C3 mice. The maps for age-matched wild-type B6C3 mice were regenerated from the data reported in Bero et al. (2012). D, Node degree in motor, somatosensory, retrosplenial, and visual cortices (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).