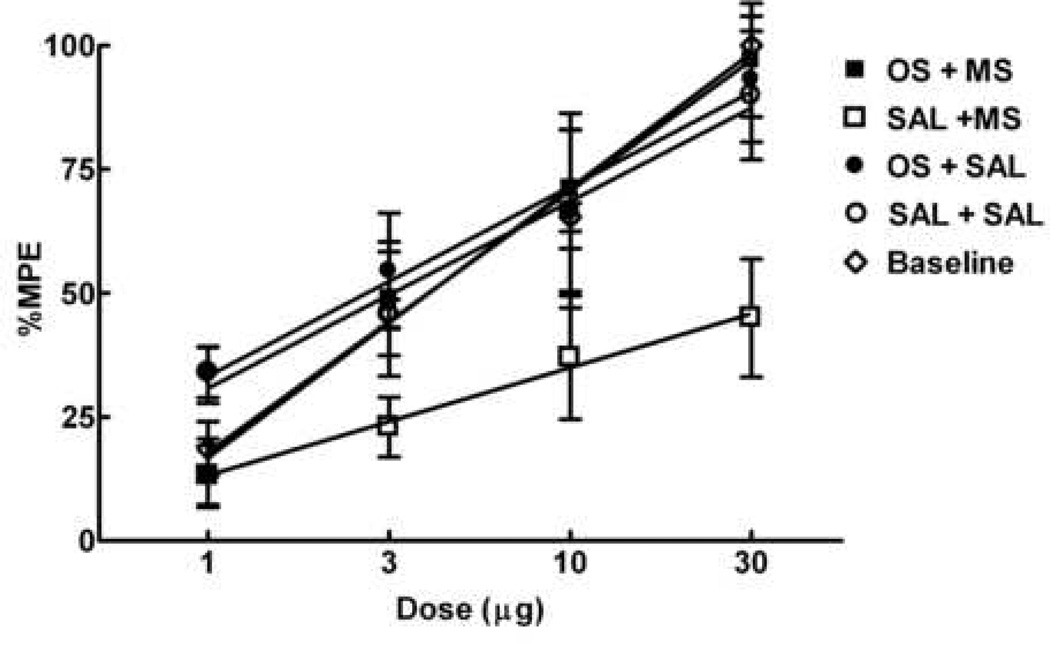
Figure 6.
Spinal administration of ondansetron reduces antinociceptive tolerance to spinal morphine induced by sustained morphine exposure. Male Sprague Dawley rats received either morphine (squares) or saline minipumps (circles). Antinociceptive dose-response functions for i.th. morphine were generated before minipump implantation (Baseline) and 6 days after minipump implantation in the 52°C water tail-flick test. Each group of rats was tested with only one dose, 30 min after i.th. morphine injection. The dose-effect curve for i.th. morphine in groups with morphine minipumps and previous i.th. injections of saline 10 min before morphine injection was shifted significantly to the right of that for animals with saline minipumps (P<0.05). The dose-effect curve of animals with morphine minipumps and previous i.th. injection of ondansetron (30 µg) was not different from that of the animals with saline minipumps or baseline. There were 6 animals per dose.