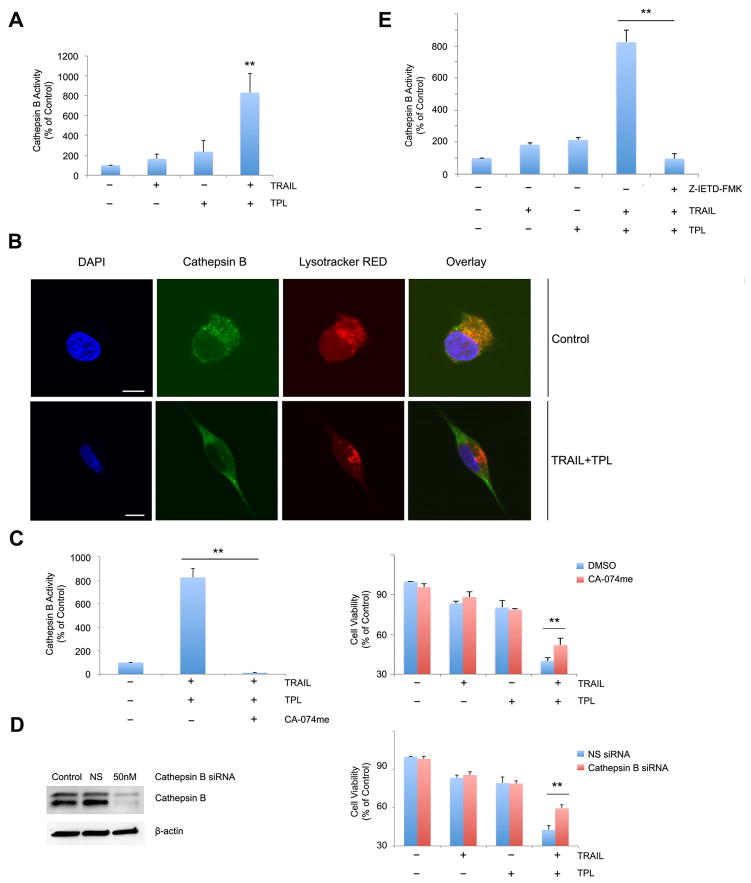
Figure 4. Combination of TRAIL and triptolide increases lysosomal membrane permeabilization in pancreatic cancer cells.
A. MIA PaCa-2 cells treated with either TRAIL or triptolide or their combination show an increase in cytosolic cathepsin B activity, suggesting lysosomal permeabilization. Cytosolic cathepsin B values are expressed as a percentage of control. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of 6 independent experiments. **p <0.01.
B. MIA PaCa-2 cells treated with a combination of TRAIL and triptolide were evaluated for presence of cytosolic cathepsin B using confocal microscopy. Cathepsin (green) colocalizes with lysosomal (lysotracker red) in a punctuate fashion in control cells, suggesting intra-lysosomal location. The nuclei have been stained with 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Treatment with TRAIL and triptolide results in diffused staining of cathepsin B and reduced co-localization with the lysosome, suggesting release of cathepsin B into the cytosol. Scale bar, 10 micron/L.
C. MIA PaCa-2 cells treated with the cathepsin B specific inhibitor, CA-074me, show a significant decrease in cathepsin B activity (left) and an increase in cell viability (right) when treated with TRAIL and triptolide. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *p < 0.01.
D. MIA PaCa-2 cells treated with a cathepsin B specific siRNA show a significant decrease in cathepsin B expression (left) and an increase in cell viability (right) when treated with TRAIL and triptolide. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of 3 independent. *p < 0.01.
E. MIA PaCa-2 cells treated with a caspase-8 inhibitor, Z-IETD-FMK and TRAIL and triptolide for 24 hours show a significant decrease in Cathepsin B activation when compared to control untreated cells. The bars represent mean ± SEM, n≥3. **p < 0.01.