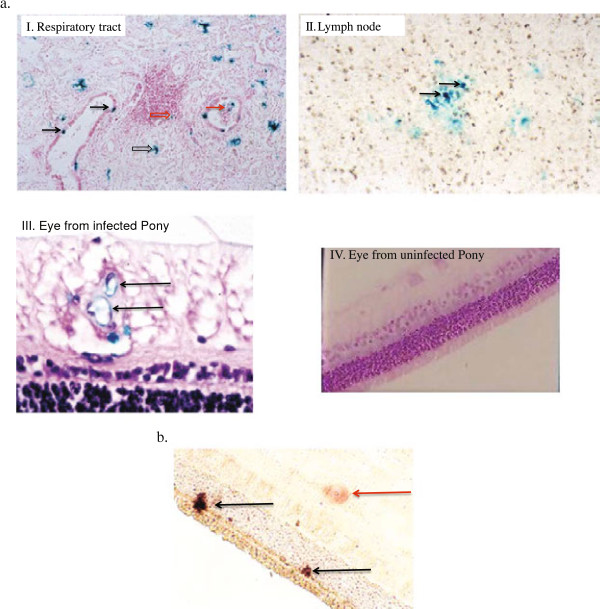
Figure 3.
Expression of LacZ indicating the presence of AB4Δ75-LacZ or EHV-1 gB DNA expression following experimental infection. A. LacZ expression as indicated by X-gal positive cells representing presence of AB4∆75-LacZ. I. Respiratory tract 24 h pi: Beta galactosidase positive bronchial epithelial cells (black solid arrows); positive airway debris (red solid arrow); positive interstitial cells (black open arrows). A positive mononuclear cell, located within a perivascular cuff, is shown by a red open arrow. H&E stain, magnification × 50. II. Section of submandibular lymph node 48 h after infection with AB4∆75-LacZ showing beta galactosidase positive mononuclear cells (black solid arrows). H&E stain, magnification × 400. III. Section of neurosensory retina 9 days after infection with AB4∆75-LacZ showing beta galactosidase positive endothelial cells (black solid arrows). H&E stain, magnification × 400. IV. Section of neurosensory retina from an uninfected pony stained with X-gal and H&E counter stain, magnification × 200. B. In situ hybridization showing transcription of the late gB gene DNA in photoreceptors of the neurosensory retina on day 12 pi. Positive photoreceptor nuclei (black solid arrows) and a single optic nerve ganglion cell nucleus (solid red arrow) are shown. No counter stain, magnification x 200.