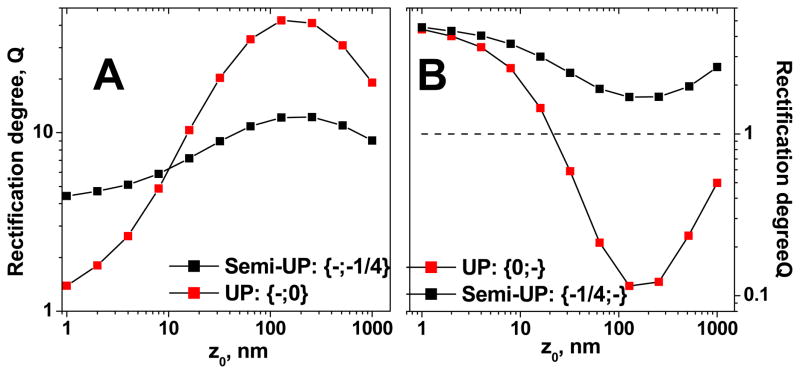
Figure 6.
Comparison of unipolar diodes (UP), which consist of a charged zone and a zone that is neutral, to semi-UP diodes, which consist of two zones with surface charge of the same sign but different density. As evidenced by our experiments, a neutral surface (σ = 0) is difficult to achieve for our pores, we calculated current-voltage curves when 75% of the surface carboxyls were converted to uncharged methoxy groups. A) Comparison of the rectification degree for {−,0} and {−;¼−} diodes. B) Rectification degrees Q for {0,−} and {¼−;−} diodes. As followed from this figure, semi-UP conical diodes are very similar in their behavior to initial conical pores, thus devices with the surface charge pattern {−;−}. The calculations were performed for L = 12μm, A = 250nm, Cbulk = 0.1M, and σ = −0.5e/nm2. The rectification degree was calculated for 1V. See text for details.