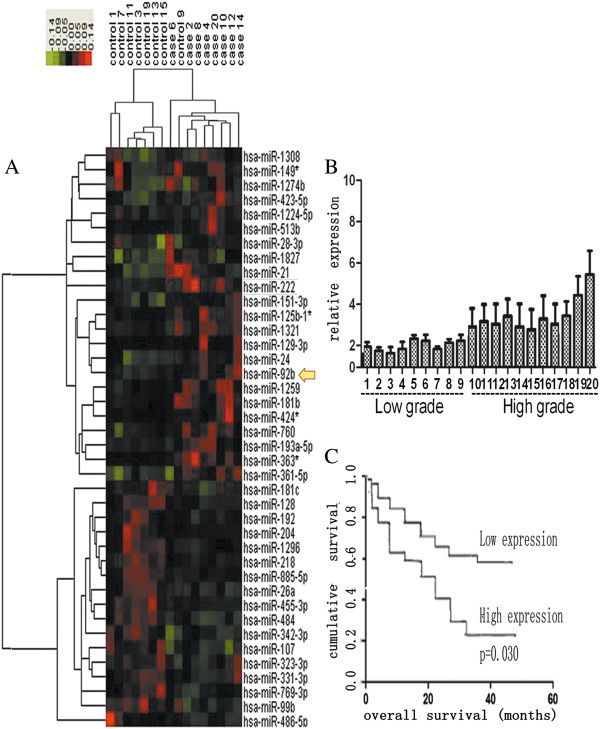
Figure 1.
Expression and clinical significance of miR-92b in gliomas. (A) A heat map diagram generated by unsupervised clustering analysis with 40 significantly deregulated miRNAs in eight human glioma tissues. The hierarchical clustering was performed with the average linkage and uncentered correlation. The miRNA expression profile effectively segregated the human glioma samples from their corresponding nontumorous tissues (frozen samples) (p<0.01). The red and green colors represent the high and low expression, respectively. (B) miR-92b expression in 20 glioma tissues assayed by real-time PCR. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for miR-92b expression. High-grade glioma patients with high levels of miR-92b had a significantly worse outcome. The expression level was categorized as low expression (final score 3) and high expression (>3). The number of patients in each group was shown: miR-92b, low expression (9 patients) and high expression (11 patients).