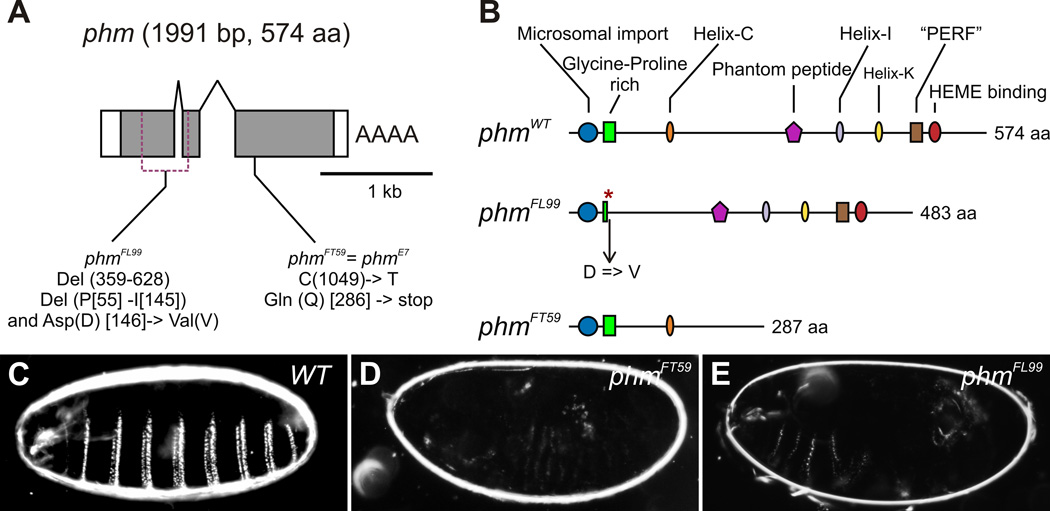
Fig. 2. FL99 and FT59 are alleles of the gene phm.
(A) Schematic representation of the intron-exon structure of phm (adopted from Niwa et al., 2004). White rectangles correspond to 5’ and 3’ UTR, grey ones indicate translated regions. The gene phm encodes for 1991 bp cDNA product or 574 amino acids long protein. In the phmFL99 allele parts of the first and the second exons are deleted from 359 bp until 628 bp removing amino acids 55–145. The phmFL99 allele carries in addition a substitution of the aromatic Aspartic acid (Asp, D) at the position 146 by the hydrophobic Valine (Val, V). The phmFT59 allele carries the same mutation as phmE7 (Niwa et al., 2004; Warren et al., 2004), a C to T point mutation at the nucleotide position 1049, leading to a formation of an in-frame stop codon at amino acid position 286. (B) Schematic diagrams illustrating phantom proteins produced by phmWT (adopted from Warren et al., 2004), phmFL99 and phmFT59 alleles. The deletion of the part of the Glycine-Proline rich domain in the phmFL99 allele is depicted by a red asterisk. (C-E) Cuticle preparation. Wild-type cuticle (C), and lack of cuticle differentiation in phmFT59 (D) and phmFL99 (E) mutant embryos.