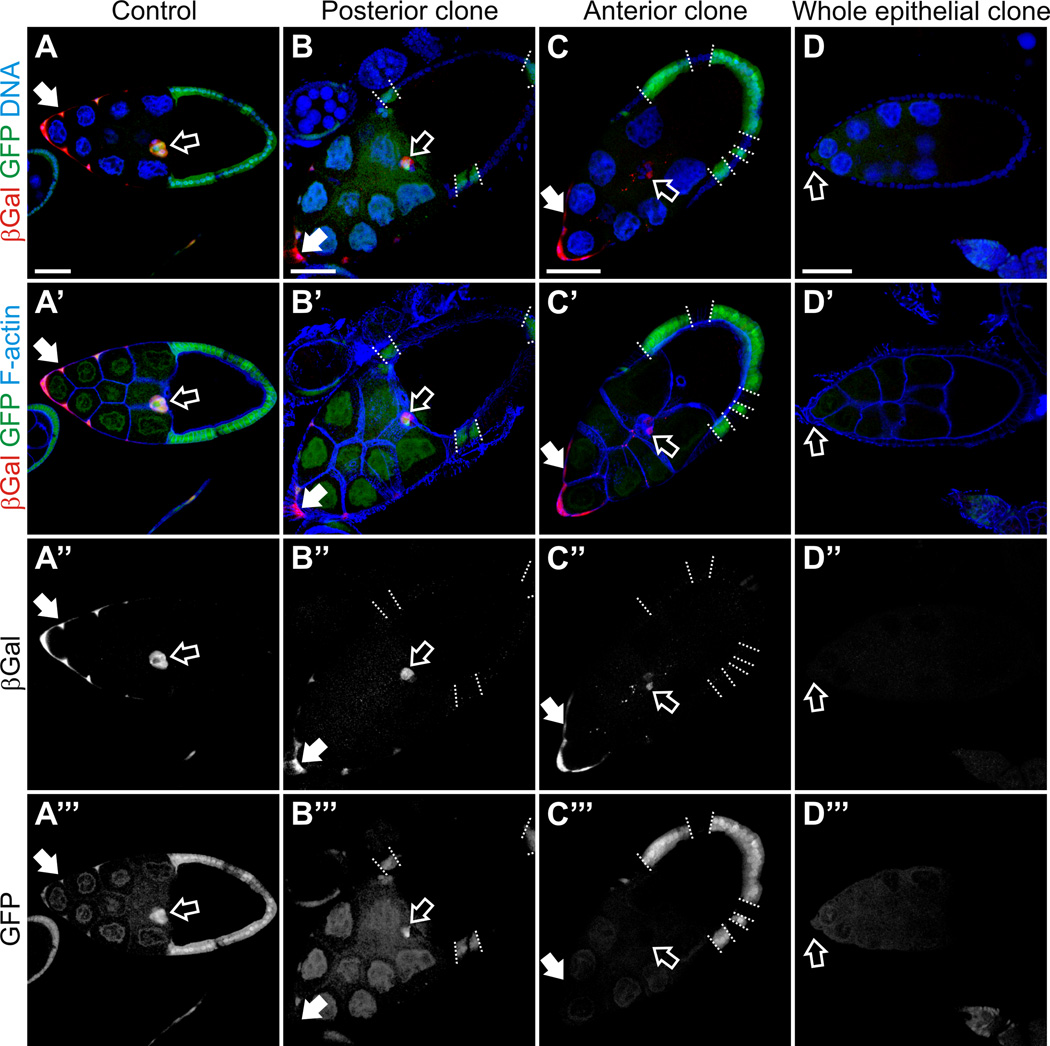
Fig. 3. Ecdysone signaling failed to be activated in the in the phmFL99 and phmFT59 whole epithelial homozygous mutant egg chambers.
Egg chambers from flies carrying EcR-lacZ reporter line in the genetic background stained with Hoechst to label nuclei, phalloidin to label F-actin, and with anti-βGal antibodies to detect activation of EcR. Egg chambers are oriented with the anterior to the left. Scale bars represent 40 µm. (A) Stage 10A wild-type egg chambers. The LacZ reporter expression was detected in the anterior FCs including the BCs (open arrow) and stretched cells overlying the nurse cells (filled arrow), which indicates that ecdysone signaling is activated in these cells types. (B, C) Mosaic phmFL99 and phmFT59 mutant egg chambers, stage 10A. phmFL99 and phmFT59 homozygous mutant clones are marked by the absence of GFP. The borders between mutant clones and neighboring wild-type cells are marked by dashed lines. Border cells are marked with open arrow, stretched cells by filled arrows. (D) We observed a lack of ecdysone signaling activation in the phmFL99 or phmFT59 homozygous mutant egg chambers containing whole epithelial mutant clones, which are marked by the absence of GFP (D’”). Border cells are marked by open arrow (D-D”’).