Figure 2.
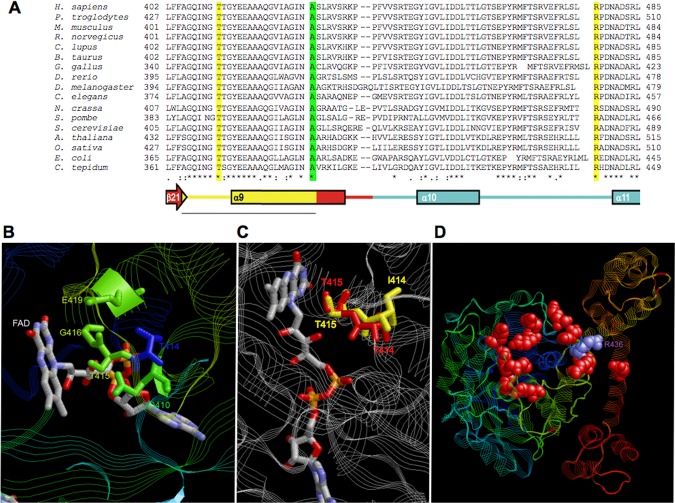
In silico structural analysis. A: Alignment of Mto1 proteins from animals, yeasts, plants, and eubacteria around mutated amino acids. In yellow the amino acids corresponding to mutations hThr411Ile and hArg477His, in green the amino acid corresponding to mutation Ala428Thr [Ghezzi et al., 2012]. The corresponding secondary structure elements for the C. tepidum GidA structure are indicated and colored according to Meyer et al. [2008]. B: Structure of the C. tepidum GidA region around the FAD moiety. Amino acids of the motif 2 of GidA which bind the FAD group are indicated. For simplicity, the numbers refer to the equivalent position in yeast Mto1. C: Structure of the C. tepidum GidA region around the FAD moiety superimposed to the model structure of GidA. The wt structure of the amino acids equivalent to threonines 414 (T414) and 415 (T415) in yeast Mto1 is in red. The predicted structure of the amino acids equivalent to yeast mutant isoleucine 414 (I414, corresponding to the human mutation Thr411Ile) and adiacent threonine 415 (T415) is in yellow. For simplicity, the numbers refer to the position in yeast Mto1. D: Overall structure of the C. tepidum GidA with basic amino acids (in red), which form a pocket who is predicted to bind the D-stem of the incoming tRNA. The bacterial Arg436 residue (R436), equivalent to hArg477 and yArg481, is in magenta.