Figure 3.
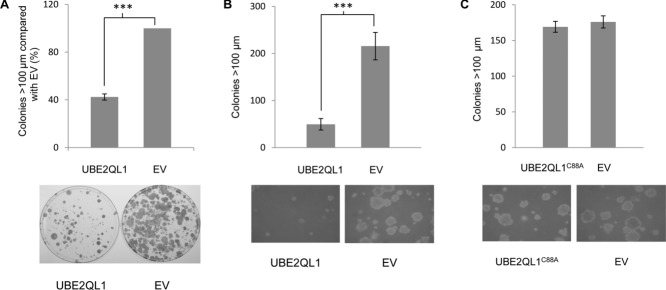
UBE2QL1 shows growth suppression and inhibition of anchorage-independent growth. A: Colony growth assays with SKRC 47 RCC cell lines stably expressing pFLAG-CMV-4 (EV) or pFLAG-CMV-4-wtUBE2QL1 (UBE2QL1). Colonies (>100 μm) were manually counted blindly after 4 weeks (t-test, error bars = SEM, ***P < 0.0001, n = 3). SKRC 47 cells not expressing UBE2QL1 (EV) produced significantly more large (>100 μm) colonies compared with those expressing exogenous UBE2QL1 (UBE2QL1). Below the graph is a representative plate showing colony reduction after UBE2QL1 reexpression. B: Stable clones of SKRC 47 pFLAG-CMV-4-wtUBE2QL1 and pFLAG-CMV-4 were seeded at the same density into soft agar and incubated for five weeks. SKRC 47 cells not expressing UBE2QL1 (EV) produced significantly more large (>100 μm) colonies compared with cells expressing exogenous UBE2QL1 (UBE2QL1) (t-test, error bars = SEM, ***P < 0.0001, n = 6). Below the graph are representative images of clones following 5 weeks of incubation (×100 magnification). C: Stable clones of SKRC 47 pFLAG-CMV-4-UBE2QL1C88A and pFLAG-CMV-4 were seeded at the same density into soft agar and incubated for five weeks. SKRC 47 cells expressing UBE2QL1C88A (UBE2QL1C88A) produced similar numbers of large (>100 μm) colonies compared with cells not expressing UBE2QL1 (EV) (t-test, error bars = SEM, P = 0.3677, n = 6). Below the graph are representative images of clones following 5 weeks of incubation (×100 magnification).
