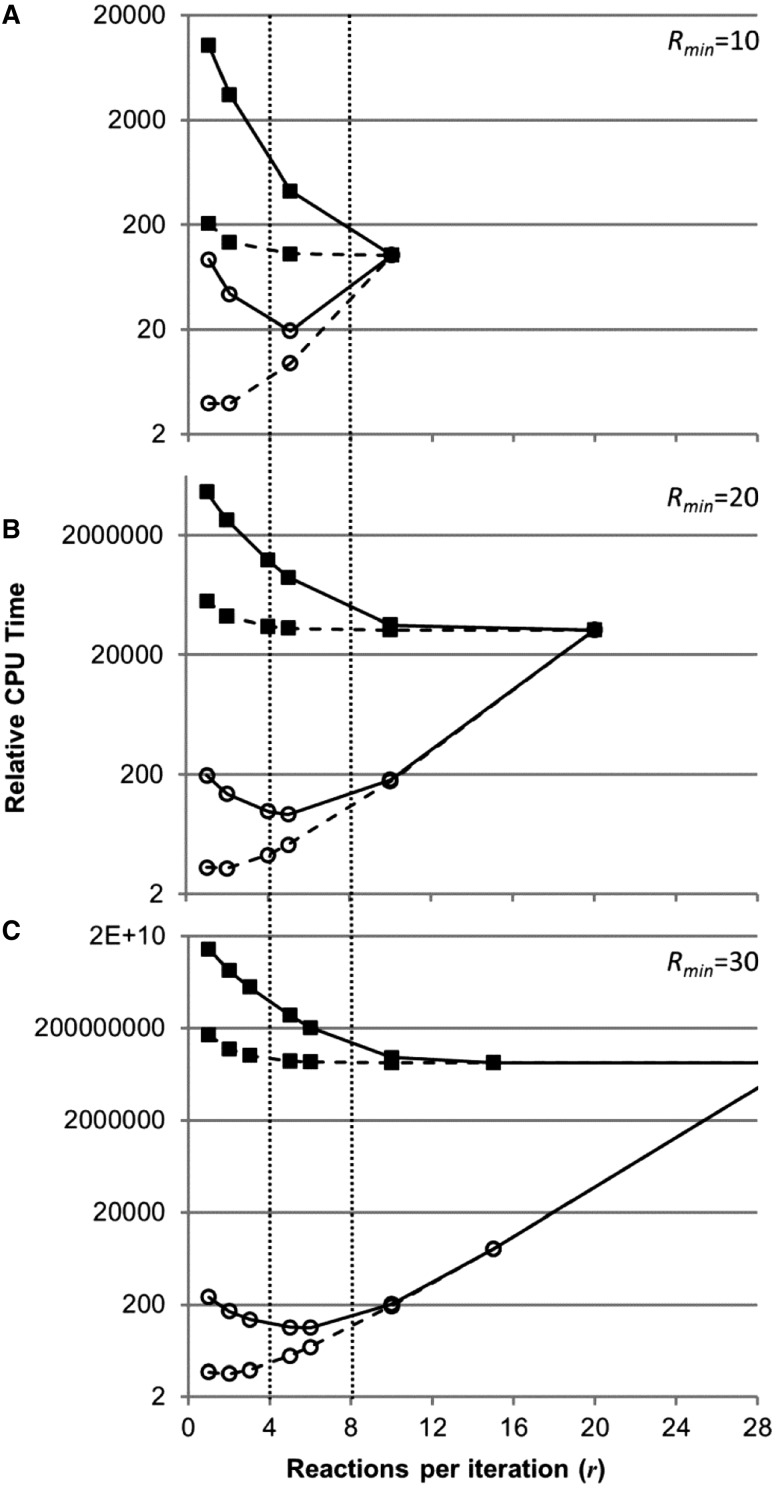
Fig. 6.
Optimization of reactions for splitting applied per iteration (r). Relative CPU time for theoretical networks requiring 10 (A), 20 (B) and 30 (C) total reactions for splitting to complete, assuming that one subnetwork is intractable per iteration (open circles) or all subnetworks are intractable until the last iteration (closed squares). Time for intractable subnetworks was varied between 10-fold increase (solid lines) and 10-fold decrease (dashed lines) relative to an unsplit model. Relative CPU time is the summation of time to complete all subnetworks normalized by time to complete the whole unsplit network. Vertical dotted lines designate the optimal working range based on the minimum (open circles with solid lines) and the exponential decrease (closed squares), given no prior knowledge of network splitting behavior