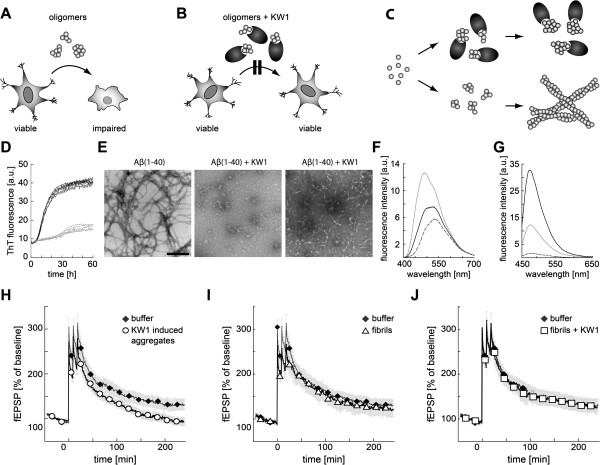
Figure 5.
Structural and biological effects of KW1 on Aβ(1–40) peptide in vitro. (A-C) Hypothetical models of KW1 activity that are considered in this work; (A-B) KW1 antagonizes the toxic effect of oligomers. (C) KW1 modifies the Aβ assembly reaction. (D) Aggregation of Aβ(1–40) monitored by time-dependent ThT fluorescence at 490 nm. Black: Aβ(1–40) alone; grey: Aβ co-incubated with KW1 (n = 5). Length of the lag-phase: 5.6 ± 0.5 h (without KW1) and 24 ± 2.7 h (with KW1). (E-G) Structural comparison of Aβ fibrils, obtained by incubation of 100 μM Aβ(1–40) in 50 mM HEPES buffer, pH 7.4, 50 mM NaCl for 5 days at 37°C, and of KW1-stabilized aggregates, obtained by co-incubation of 100 μM Aβ(1–40) with 20 μM KW1 under the same conditions. (E) Negative stain TEM images. Different regions of the grid of KW1-induced aggregates are shown. Scale bar represents 200 nm. (F) ANS and (G) ThT fluorescence spectra recorded with KW1-stabilized Aβ aggregates (grey) or Aβ fibrils (black). Dashed spectra: dye without protein. (H) KW1-induced aggregates, obtained by co-incubation of Aβ(1–40) with KW1 for 5 days, potently reduces the LTP response (p = 0.029, estimated with repeated-measures ANOVA). (I) LTP measurement with slices pre-treated with Aβ(1–40) fibrils, obtained by a 5-day incubation of the pure peptide, shows no significant deviation from the buffer control. (J) Addition of KW1 to these fibrils 15 min prior to addition to the slice does not modify this result. Error bars (grey) represent standard error of the mean (n = 8-20).