Figure 1.
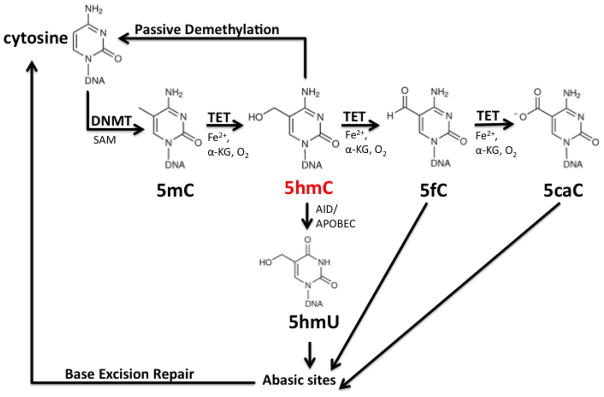
Chemistry of DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation. 5methylcytosine (5-mC) is produced from the addition of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) onto the 5-carbon of Cytosine by DNA methyltransferases (DNMT). Ten-eleven-translocation (TET) proteins then catalyze the interactive oxidation of 5mC to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC), 5-formlycytosine (5-fC) and 5-carboxycytosine (5-caC), with required cofactors alpha-ketoglutarate (a-KG), Iron (Fe2+) and oxygen. 5-hmC, 5-fC or 5-caC could act as an intermediate in both passive and active DNA demethylation pathways involving DNA repair enzymes like AID or APOBEC (activation-induced cytidine deaminase).
