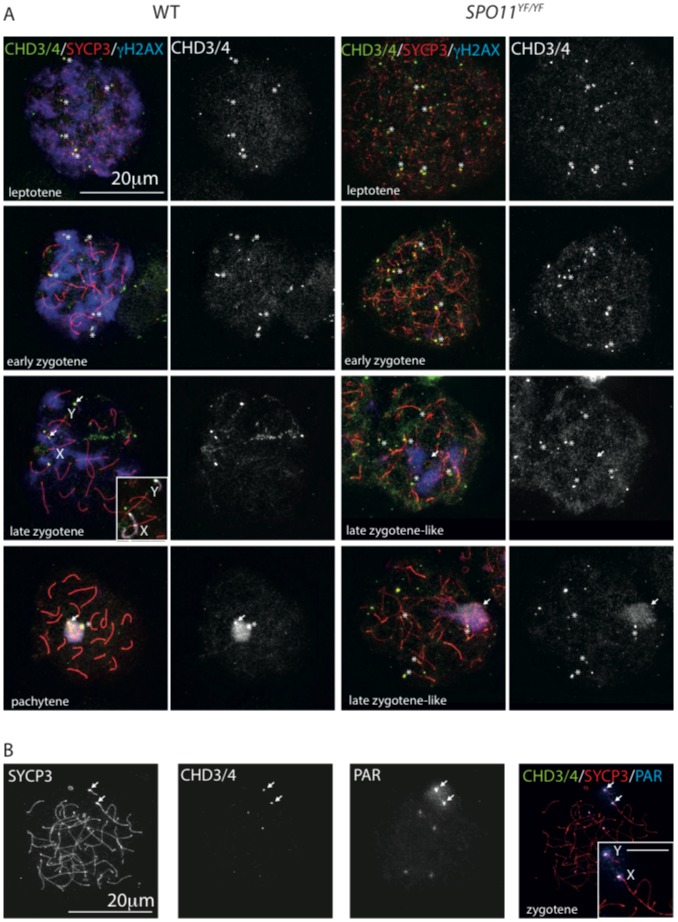
Figure 6. CHD3/4 localisation in spermatocytes is independent of SPO11.
(A) Spread wild type (left) and Spo11 null (Spo11YF/YF, right) spermatocytes stained for CHD3/4 (green), SYCP3 (red), and γH2AX (blue), the single CHD3/4 staining is shown in white to the right of each merge. In wild type nuclei, CHD3/4 does not colocalise with γH2AX in leptotene and zygotene. Specific foci accumulate on some chromosome ends (asterisks indicate examples), in particular on the pseudoautosomal region (PAR) of both X and Y, as can be observed in the late zygotene nucleus (white arrows). The inserted image shows part of the same nucleus with the X and Y chromosomal axes in white, for easy recognition. In pachytene, γH2AX and CHD3/4 colocalize on the XY body whereby CHD4 is particularly enriched on the PAR (white arrow) and the X centromere (asterisk). In Spo11 null spermatocytes enrichment of CHD3/4 is observed on some chromosome ends in early zygotene (asterisks indicate examples), and in the pseudo XY body (white arrow) of later zygotene-like spermatocytes. (B) Spread Spo11 null zygotene spermatocyte stained for SYCP3 and CHD3/4, and hybridized with a BAC probe recognizing the PAR. In the merge, an enlargement of the region encompassing the X and Y is shown (scale bar indicates 5 µm). In this nucleus CHD3/4 stain the PAR of the X and Y, but also mark the ends of 4 additional chromosome ends, that are also recognized, to a lesser extent, by the PAR probe. It is not clear what causes this crossreaction (see Materials and Methods).