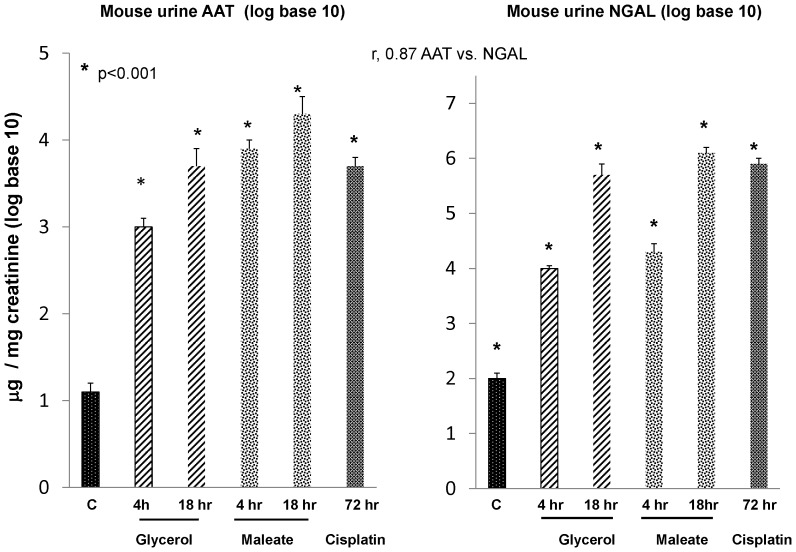
Figure 8. Each of the experimental AKI models induced prompt and massive increases in urinary AAT protein levels, and these increases were comparable to, or exceeded those, observed for urinary NGAL, a classic AKI biomarker protein.
All values were factored for urinary creatinine concentrations and are presented as log base 10. Massive urinary AAT protein increases were observed, rising from control values of ∼10 to as high as 30,000 µg/mg creatinine within just 4 hrs of AKI induction (left panel). Furthermore, these values were sustained at each of the tested delayed time points. Of note, these AAT increases were as great, if not greater, than those observed for NGAL (right panel), and a strong correlation (r, 0.87) between AAT vs. NGAL levels was observed.