Figure 4.
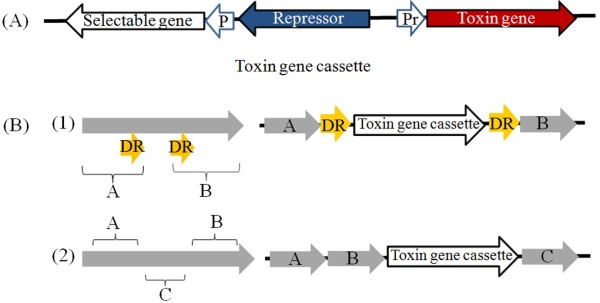
Toxin gene-based genetic engineering strategies. (A) Schematic representation of the toxin gene cassette. P: Commonly-used constitutive promoter. Pr: Promoter of operator-repressor system, which is repressed by the repressor and activated by an inducer e.g. Pspac, Pxyl. The repressor gene in the cassette can also be deleted in some methods. (B) Two different strategies based on toxin gene cassettes. A: upstream sequence; B: downstream sequence; C: sequence for integration of the toxin gene cassette, in combination with A in (2); DR: direct repeat sequence. After integration of the toxin gene cassette into a target chromosome locus via double-crossover recombination [A and B in (1) or A and C in (2)] and positive selection for antibiotic resistance, the cassette is removed by a single crossover event between two DR sequences in (1) or B sequences in (2).
