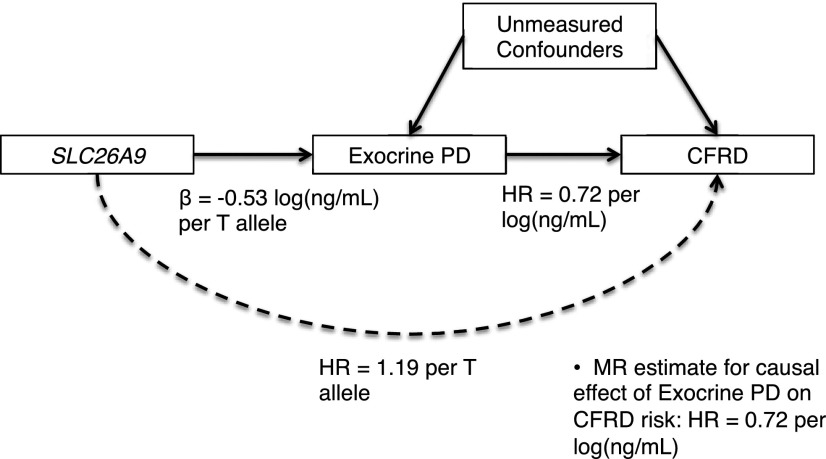
Figure 2.
MR framework. MR estimate of causal effect of prenatal exocrine PD on CFRD risk was obtained by dividing the coefficient from the regression of CFRD diagnosis age on rs7512462 genotype, loge(HR 1.19), by the average increase in loge(IRT) at birth per additional SLC26A9 rs7512462 risk allele, β = −0.53, yielding: loge(HRcausal) = loge(1.19)/(−0.53) = −0.33. Exponentiation provided an HRcausal of 0.72. This causal effect estimate of the HR was equivalent to the estimate obtained by directly regressing CFRD diagnosis age on loge(IRT) at birth (HR 0.72). Application of MR required that the SLC26A9 instrument be robustly associated with the exposure and independent of confounding factors; these were satisfied by our F statistic of 8.99 and Mendel’s law of independent assortment, respectively. Additionally, it was assumed that the relationship between rs7512462 and CFRD was mediated by prenatal exocrine PD (see Discussion).