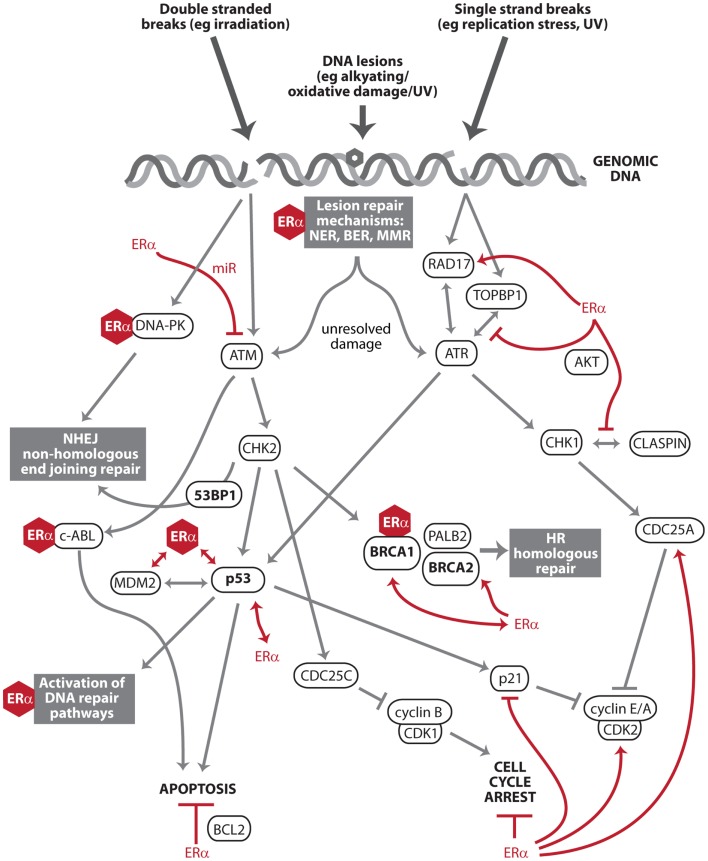
Figure 1.
Key effectors of the DNA damage response and DNA repair that intersect with estrogen receptor α signaling. The DNA damage response (DDR) is a series of pathways that recognize and process DNA damage. After DNA damage recognition, signals are transduced and amplified through kinase activation (ATM, ATR, DNA-PK, CHK1, and CHK2) to downstream effectors (e.g., p53 and BRCA1) that facilitate DNA repair, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest. Estrogen receptor α (ERα) exists in complex with multiple members of the DDR and DNA repair pathways (e.g., DNA-PK, BRCA1, p53, and MDM2). These protein:protein interactions are denoted by ERα represented as a hexagon. This includes c-Abl, a multi-functional regulator of the DDR and its downstream pathways (14). ERα also transcriptionally regulates or is regulated by other members of these pathways (e.g., ATM, ATR, CHK1, BRCA2, and DNA damage checkpoint protein Rad17), denoted by red lines. ERα signaling antagonizes two major endpoints of DDR action: apoptosis and cell cycle arrest (red lines).