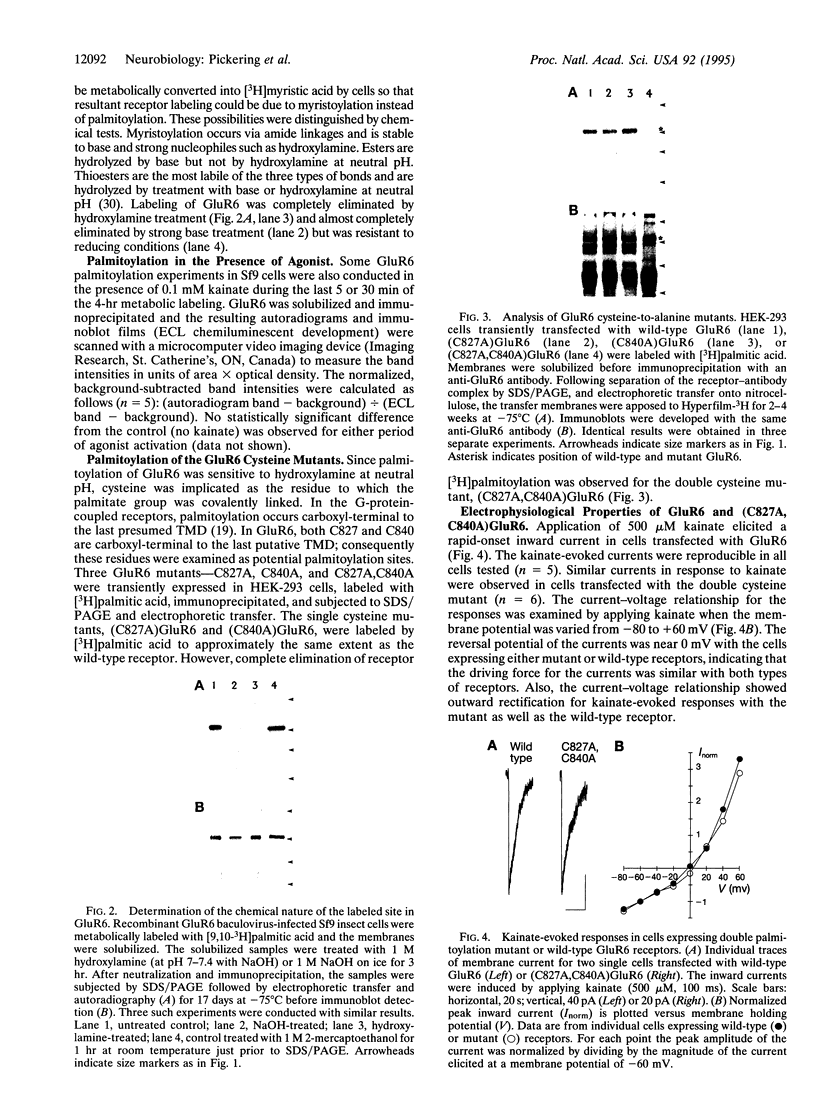
Abstract
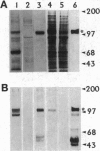
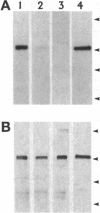
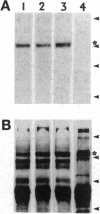
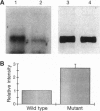
The G-protein-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR1 alpha and the ionotropic glutamate receptor GluR6 were examined for posttranslational palmitoylation. Recombinant receptors were expressed in baculovirus-infected insect cells or in human embryonic kidney cells and were metabolically labeled with [3H]palmitic acid. The metabotropic mGluR1 alpha receptor was not labeled whereas the GluR6 kainate receptor was labeled after incubation with [3H]palmitate. The [3H]palmitate labeling of GluR6 was eliminated by treatment with hydroxylamine, indicating that the labeling was due to palmitoylation at a cysteine residue via a thioester bond. Site-directed mutagenesis was used to demonstrate that palmitoylation of GluR6 occurs at two cysteine residues, C827 and C840, located in the carboxyl-terminal domain of the molecule. A comparison of the electrophysiological properties of the wild-type and unpalmitoylated mutant receptor (C827A, C840A) showed that the kainate-gated currents produced by the unpalmitoylated mutant receptor were indistinguishable from those of the wild-type GluR6. The unpalmitoylated mutant was a better substrate for protein kinase C than the wild-type GluR6 receptor. These data indicate that palmitoylation may not modulate kainate channel function directly but instead affect function indirectly by regulating the phosphorylation state of the receptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alaluf S., Mulvihill E. R., McIlhinney R. A. The metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR4, but not mGluR1 alpha, is palmitoylated when expressed in BHK cells. J Neurochem. 1995 Apr;64(4):1548–1555. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64041548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Gironès N., Davis R. J. Inhibition of the receptor-mediated endocytosis of diferric transferrin is associated with the covalent modification of the transferrin receptor with palmitic acid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16644–16655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M., Hannun Y., Loomis C. Mixed micelle assay of protein kinase C. Methods Enzymol. 1986;124:353–359. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)24027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. A., Dingledine R. Topology profile for a glutamate receptor: three transmembrane domains and a channel-lining reentrant membrane loop. Neuron. 1995 Feb;14(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Chidiac P., Hebert T. E., Loisel T. P., Moffett S., Mouillac B. Dynamic palmitoylation of G-protein-coupled receptors in eukaryotic cells. Methods Enzymol. 1995;250:300–314. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)50080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildy-Mayfield J. E., Harris R. A. Activation of protein kinase C inhibits kainate-induced currents in oocytes expressing glutamate receptor subunits. J Neurochem. 1994 Apr;62(4):1639–1642. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62041639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eason M. G., Jacinto M. T., Theiss C. T., Liggett S. B. The palmitoylated cysteine of the cytoplasmic tail of alpha 2A-adrenergic receptors confers subtype-specific agonist-promoted downregulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11178–11182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T., Stroud E., Whatley R. E., Prescott S. M., Muszbek L., Laposata M., McEver R. P. P-selectin is acylated with palmitic acid and stearic acid at cysteine 766 through a thioester linkage. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11394–11400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herb A., Burnashev N., Werner P., Sakmann B., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The KA-2 subunit of excitatory amino acid receptors shows widespread expression in brain and forms ion channels with distantly related subunits. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Maron C., Heinemann S. N-glycosylation site tagging suggests a three transmembrane domain topology for the glutamate receptor GluR1. Neuron. 1994 Dec;13(6):1331–1343. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90419-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houamed K. M., Kuijper J. L., Gilbert T. L., Haldeman B. A., O'Hara P. J., Mulvihill E. R., Almers W., Hagen F. S. Cloning, expression, and gene structure of a G protein-coupled glutamate receptor from rat brain. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1318–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.1656524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R., Bhatnagar R. S., Knoll L. J., Gordon J. I. Genetic and biochemical studies of protein N-myristoylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:869–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. E., Limbird L. E. Mutations of the alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor that eliminate detectable palmitoylation do not perturb receptor-G-protein coupling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8003–8011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett S., Mouillac B., Bonin H., Bouvier M. Altered phosphorylation and desensitization patterns of a human beta 2-adrenergic receptor lacking the palmitoylated Cys341. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):349–356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouillac B., Caron M., Bonin H., Dennis M., Bouvier M. Agonist-modulated palmitoylation of beta 2-adrenergic receptor in Sf9 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21733–21737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kleuss C., Gilman A. G. Receptor regulation of G-protein palmitoylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng G. Y., George S. R., Zastawny R. L., Caron M., Bouvier M., Dennis M., O'Dowd B. F. Human serotonin1B receptor expression in Sf9 cells: phosphorylation, palmitoylation, and adenylyl cyclase inhibition. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 2;32(43):11727–11733. doi: 10.1021/bi00094a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng G. Y., Mouillac B., George S. R., Caron M., Dennis M., Bouvier M., O'Dowd B. F. Desensitization, phosphorylation and palmitoylation of the human dopamine D1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Mar 15;267(1):7–19. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng G. Y., O'Dowd B. F., Caron M., Dennis M., Brann M. R., George S. R. Phosphorylation and palmitoylation of the human D2L dopamine receptor in Sf9 cells. J Neurochem. 1994 Nov;63(5):1589–1595. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63051589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Palmitoylation of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Mutation of Cys341 in the carboxyl tail leads to an uncoupled nonpalmitoylated form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7564–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Glaser L., Merlie J. P. Alpha and beta subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor contain covalently bound lipid. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5364–5367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Bogachuk A. S. Two adjacent cysteine residues in the C-terminal cytoplasmic fragment of bovine rhodopsin are palmitylated. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering D. S., Thomsen C., Suzdak P. D., Fletcher E. J., Robitaille R., Salter M. W., MacDonald J. F., Huang X. P., Hampson D. R. A comparison of two alternatively spliced forms of a metabotropic glutamate receptor coupled to phosphoinositide turnover. J Neurochem. 1993 Jul;61(1):85–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond L. A., Blackstone C. D., Huganir R. L. Phosphorylation and modulation of recombinant GluR6 glutamate receptors by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):637–641. doi: 10.1038/361637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche K. W., Raymond L. A., Blackstone C., Huganir R. L. Transmembrane topology of the glutamate receptor subunit GluR6. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):11679–11682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. M., Taverna F. A., Pickering D. S., Wang L. Y., MacDonald J. F., Pennefather P. S., Hampson D. R. Expression of functional metabotropic and ionotropic glutamate receptors in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Neurosci Lett. 1994 May 23;173(1-2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M. W., Hicks J. L. ATP-evoked increases in intracellular calcium in neurons and glia from the dorsal spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 2):1563–1575. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01563.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverna F. A., Wang L. Y., MacDonald J. F., Hampson D. R. A transmembrane model for an ionotropic glutamate receptor predicted on the basis of the location of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14159–14164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. Y., Salter M. W., MacDonald J. F. Regulation of kainate receptors by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphatases. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1132–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.1653455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. Y., Taverna F. A., Huang X. P., MacDonald J. F., Hampson D. R. Phosphorylation and modulation of a kainate receptor (GluR6) by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1173–1175. doi: 10.1126/science.8382377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner P. B., Bourne H. R. Activation and depalmitoylation of Gs alpha. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner P. B., Chu D. H., Wilson P. T., Levis M. J., Bourne H. R. Palmitoylation is required for signaling functions and membrane attachment of Gq alpha and Gs alpha. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25001–25008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenthold R. J., Trumpy V. A., Zhu W. S., Petralia R. S. Biochemical and assembly properties of GluR6 and KA2, two members of the kainate receptor family, determined with subunit-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1332–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wo Z. G., Oswald R. E. Transmembrane topology of two kainate receptor subunits revealed by N-glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7154–7158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]