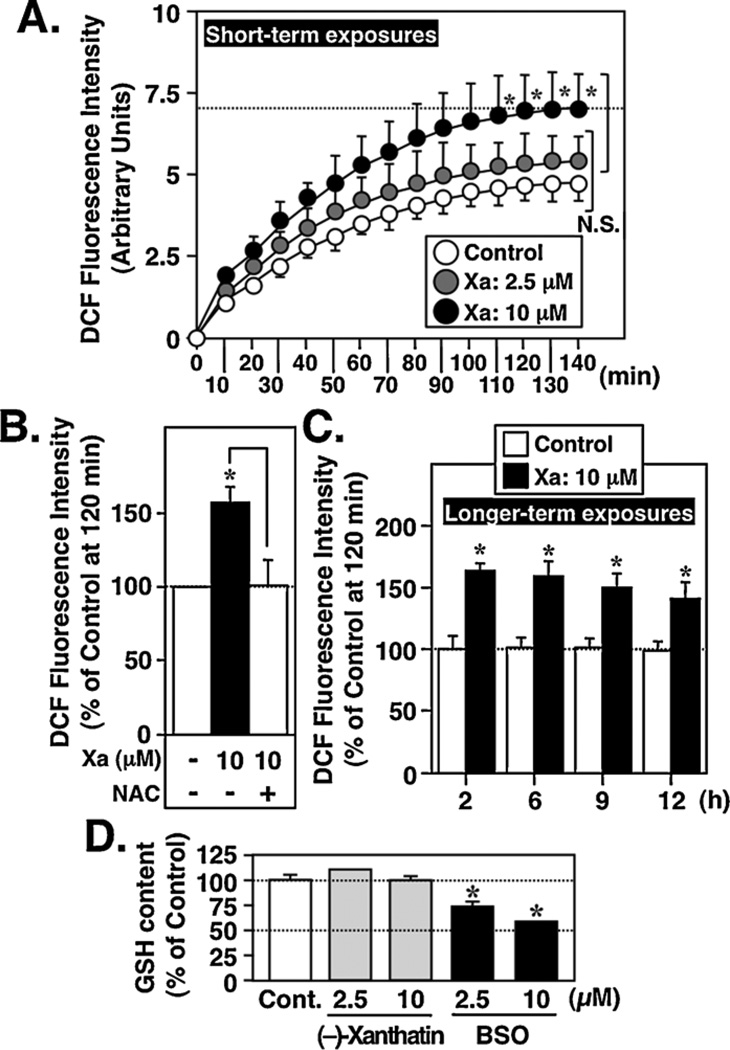
Fig. 6.
(−)-Xanthatin produces intracellular ROS as a function of time. (A) (Short-term exposures) MDA-MB-231 cells were exposed for up to 140 min to (−)-xanthatin (Xa; 2.5, 10 µM). Intracellular ROS were measured as described in Section 2. Data are expressed as the percent of vehicle-treated group (Control), as mean ± S.D. (n = 6). *Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the control. N.S., not significant. (B) MDA-MB-231 cells were exposed for 2 h to (−)-xanthatin (Xa; 10 µM) in the presence or absence of 1 mM NAC. Intracellular ROS were measured as described in Section 2. *Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the control at 120 min. (C) (Longer-term exposures) MDA-MB-231 cells were exposed for up to 12 h to (−)-xanthatin (Xa; 10 µM). Intracellular ROS were measured as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as the percent of vehicle-treated group (control), as mean ± S.D. (n = 6). *Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the control at 120 min. (D) Effect of (−)-xanthatin on the GSH levels in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cells were treated with 2.5 or 10 µM (−)-xanthatin, or 2.5 or 10 µM BSO, for 12 h and the levels of GSH were measured. Data are expressed as the percent of vehicle-treated group (indicated as Cont.), as mean ± S.D. (n = 6). *Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the control.