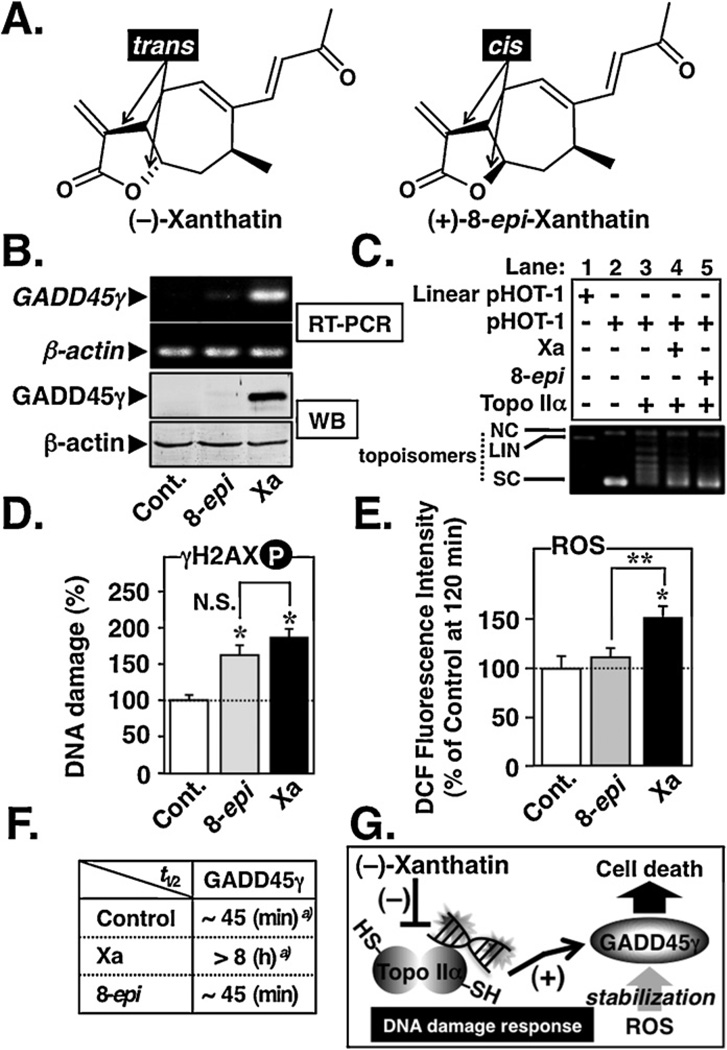
Fig. 9.
Topo IIα inhibition followed by ROS generation is involved in the (−)-xanthatin’s up-regulation of GADD45γ. (A) Chemical structures of (−)-xanthatin (trans) and its cis-isomer (+)-8-epi-xanthatin. These xanthanolies contain the exo-methylene lactone moiety in their structures. (B) RT-PCR (upper panel) and Western blot (WB, lower panel) analyses of GADD45γ levels in MDA-MB-231 cells 48 h after treatment with 10 µM (−)-xanthatin (Xa), (+)-8-epi-xanthatin (8-epi), or vehicle (Cont.). β-Actin was used the internal loading control. The number of optimized PCR cycles used for the amplification of GADD45γ and β-actin were 33 and 29, respectively. (C) Effects of 100 µM Xa or 8-epi on the DNA relaxation (pHOT-1) catalyzed by human Topo IIα. NC, nicked open circular DNA; LIN, linear DNA; SC, supercoiled DNA; topoisomers, relaxed forms of DNA. (D) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 10 µM (−)-Xa or 8-epi for 12 h. DNA damage was determined by ELISA using an anti-phospho-H2AX (Ser139) antibody. Data are expressed as the percent of the control, as mean ± S.D. (n = 6). *Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the vehicle-treated group (Cont.). N.S., not significant. (E) MDA-MB-231 cells were exposed for 2 h to 10 µM Xa or 8-epi. Intracellular ROS were measured as described in Section 2. *Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the vehicle-treated control (Cont.). **Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the 8-epi-treated group. (F) Summary of the effects of 10 µM Xa or 8-epi on the GADD45γ mRNA stability in MDA-MB-231 cells. For the data of vehicle-treated group (Control)a) and Xaa) presented in the figure, half-life data (t1/2) were taken from Fig. 7. Determination of the GADD45γ mRNA stability after 8-epi treatment was performed as described in Fig. 7. (G) A working model for the (−)-xanthatin-mediated up-regulation of tumor suppressor GADD45γ. In this study, it was revealed that (−)-xanthatin requires “two pathways” to stimulate GADD45γ expression that is highly suppressed in human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells: (i) (−)-xanthatin inhibits catalytic activity of Topo IIα (accompanied by DNA damage) through interaction with –SH residues on the molecule, followed by GADD45γ induction, and (ii) the up-regulated GADD45γ mRNA/GADD45γ protein is stabilized by concomitantly generated ROS.