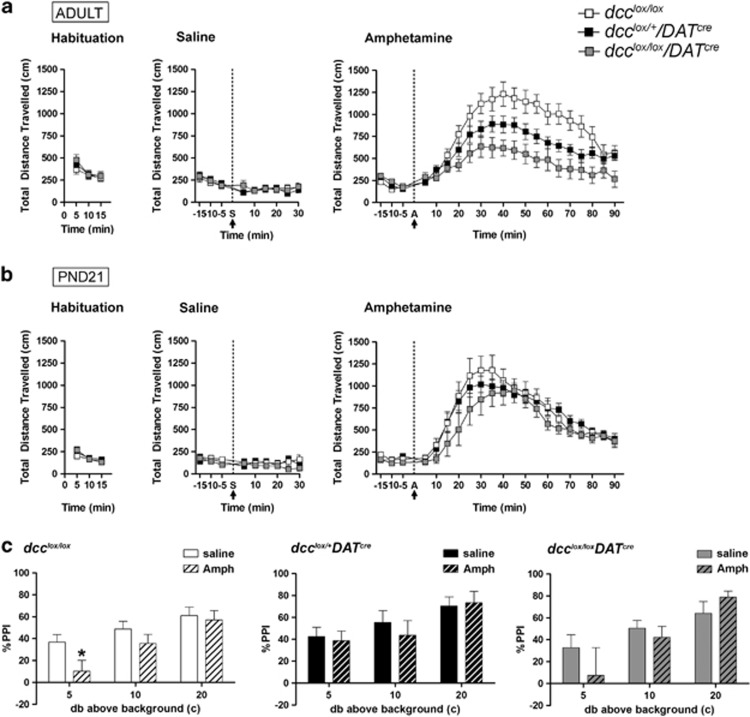
Figure 4.
dcc conditional mice exhibit blunted behavioral responses to amphetamine only in adulthood. (a) There were no differences across genotypes in locomotor activity, either at baseline (dcclox/lox: n=11; dcclox/+DATcre: n=12; dcclox/loxDATcre: n=7; two-way repeated measures ANOVA, no significant main effect of genotype: F(2,26)=0.1123, P=0.894; no significant interaction: F(4,52)=0.996, P=0.418) or following a single injection of saline (two-way repeated measures ANOVA, no significant main effect of genotype: F(2,26)=0.481, P=0.623; no significant interaction: F(16,208)=0.786, P=0.70). However, dcc conditional mice (dcclox/+DATcre and dcclox/loxDATcre) exhibited reduced locomotor activity following an acute injection of amphetamine relative to dcc-floxed control littermates (two-way repeated measures ANOVA, significant main effect of genotype: F(2, 27)=6.747, P=0.0042; significant interaction: F(40, 540)=5.104, P<0.0001). (b) Remarkably, juvenile dcc conditional mice did not exhibit blunted responses to amphetamine. No significant differences were observed across genotypes in locomotor activity at baseline (two-way repeated measures ANOVA, no significant main effect of genotype: F(2, 42)=0.528, P=0.597; no significant interaction: F(4,42)=1.085, P=0.376), following a single injection of saline (two-way repeated measures, no significant main effect of genotype: F(2,168)=0.912, P=0.417; no significant interaction: F(16,168)=0.979, P=0.481), or following a single acute injection of amphetamine (two-way repeated measures ANOVA, no significant main effect of genotype: F(2, 420)=1.072, P=0.36; no significant interaction: F(40, 420)=0.894, P=0.657). (c) dcc conditional mice exhibited resilience to amphetamine-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating. dcc-floxed littermate controls exhibited an impairment in pre-pulse inhibition at lower pre-pulses following an amphetamine (2.8 mg kg−1) challenge (dcclox/loxamph: n=10, dcclox/loxsaline; n=9 two-way repeated measures ANOVA, main effect of treatment: F(1,17)=1.68, P=0.212; significant interaction: F(17, 85)=3.01, P=0.0149. A post hoc ANOVA test for simple effects indicated a significant effect of treatment at the 5 db prepulse (F(1,102)=4.48, P=0.0443). However, amphetamine did not produce a deficit in prepulse inhibition in dcclox/+DATcre or dcclox/loxDATcre mice (dcclox/+DATcreamph: n=8, dcclox/+DATcresaline: n=9; two-way repeated measures ANOVA, no main effect of treatment: F(1,15)=0.0, P=0.987, no significant interaction: F(5,75) =.78, P=0.569; dcclox/loxDATcreamph: n=8, dcclox/loxDATcresaline: n=8; two-way repeated measures ANOVA, no main effect of treatment: F(1,14)=0.31, P=0.588, no significant interaction: F(5,70)=2.03, P=0.085).