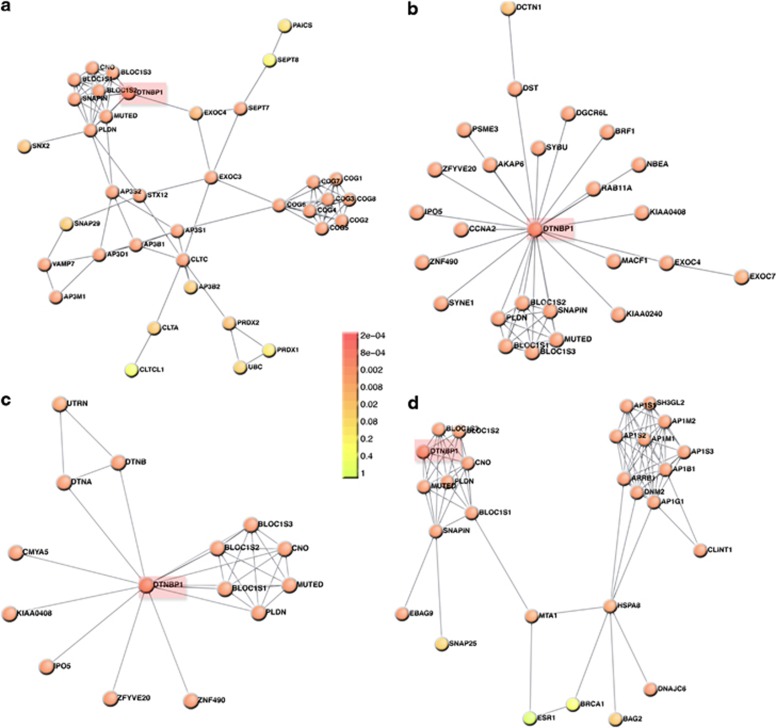
Figure 1.
DTNBP1–dysbindin interactomes differ in their constituents and topology. Interactomes were assembled with the Dapple algorithm (http://www.broadinstitute.org/mpg/dapple/dapple.php)54 using as inputs the dysbindin associated proteins identified by affinity chromatography (a), and interactors reported in three protein–protein interaction databases: (b) Biogrid (http://thebiogrid.org/), (c) Genemania (http://www.genemania.org/) and (d) String 9.05 (http://string.embl.de/). Red boxes highlight DTNBP1. Note that the identity of interacting proteins differs among interactomes. Color code represents a Dapple estimated probability that a protein would be as connected to other proteins (directly or indirectly) by chance as is depicted. Only interactome A presents a biochemically and genetically confirmed interaction between the adaptor complex AP-3 and the dysbindin-containing BLOC-1 complex.