Figure 2.
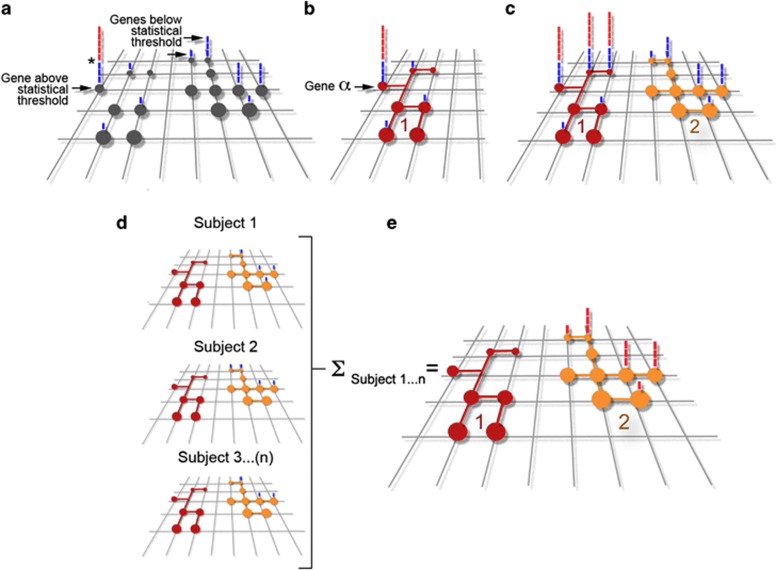
Models of cross-fertilization between genomes, proteomes and interactomes. Grid in diagrams (a) to (e) depicts a polygenic genetic landscape associated with a NDD. Circles represent defined genes within the grid that when affected in different combinations trigger a NDD. Bars above each gene indicate a subject where a gene defect was found on a GWAS. Blue bars are those subjects that have a defect in a gene below statistical threshold, which is marked by the asterisk in (a). Red bars above a gene represent subjects that have a defect in a gene above statistical threshold. (b) Depicts a ‘tip of the iceberg gene α' and the network to which it belongs represented by the connected red circles (interactome 1). (c) Depicts three ‘tip of the iceberg genes' and the network to which they belong (interactome 1). The yellow interactome 2 is constituted by genes below statistical threshold as defined by gene-centric GWAS statistical analysis. (d) Represents genetic defects (blue bars) in two interactomes per patient (subjects 1–3). Note that in all patients there are no gene defects in the red interactome. E depicts hypothetical results of an interactome-centric GWAS that includes subjects 1–3 in (d). The yellow interactome 2 is now above statistical threshold as defined by an interactome-centric GWAS statistical analysis. See text for details.