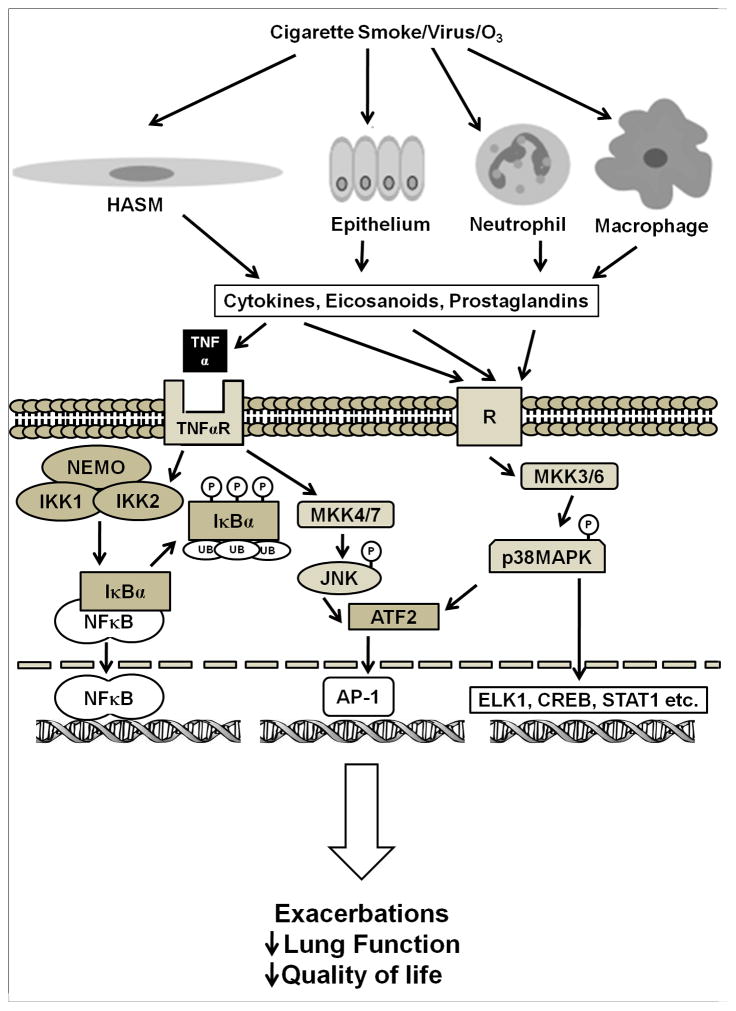
Figure 1.
Role of TNFα, IKK2 and p38MAPK in modulating gene expression. Multiple stimuli induce p38MAPK phosphorylation, including inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress. Once activated, p38 can activate multiple transcription factors including AP-1, ATF2, and ELK 1 to modulate gene transcription. TNFα binds its receptor and causes activation of NFκB by activating the IKK complex. IKK2 phosphorylates and inactivates IκBα, exposing the nuclear localization of NFκB and activating it. This figure is a simplification of the pathways involved with these mediators; multiple NFκB inducers have been identified including IL-1β and LPS, and there are interactions among kinases and transcription factors that are not elaborated here. ATF2 – activating transcription factor 2; CREB – cAMP response element binding; ELK1 – extracellular signal regulated-like kinase 1; IKK- IκB kinase; JNK – c-Jun N-terminal Kinase ; MAPK – mitogen-activated protein kinase, MKK- mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; NEMO - NFκB essential modulator ; R – prototype receptor (e.g. cytokine, eicosanoid, prostaglandin), STAT1 – signal transducers and activators of transcription 1; TNF- Tumor necrosis factor alpha, TNFR – TNF receptor.