FIG 5 .
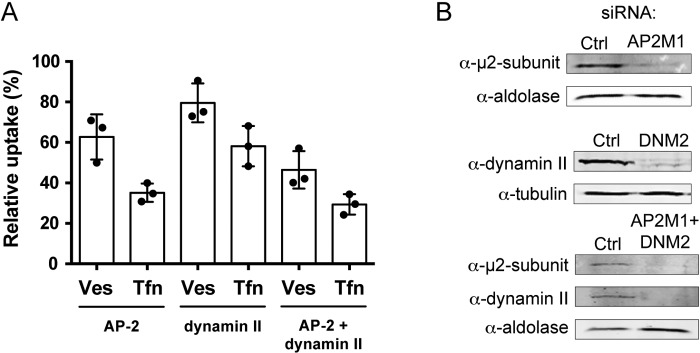
Cells depleted of AP-2 and dynamin II show reduced uptake of H. pylori vesicles. (A) H. pylori vesicles were incubated with siRNA-transfected AGS cells for 20 min. In comparison to vesicle uptake in AGS cells transfected with negative siRNA (100%), vesicle internalization was affected as follows in the knockdowns: AP-2, 63%; dynamin II, 80%; AP-2 plus dynamin II, 46%. In comparison to Tfn uptake in AGS cells transfected with negative siRNA (100%), Tfn internalization was affected as follows in the knockdowns: AP-2, 35%; dynamin II, 58%; AP-2 plus dynamin II, 29%. All experiments were performed in triplicate (n = 3). Statistical significance was as follows: with AP-2, P for Ves was 0.0039 and P for Tfn was 0.0039; for dynamin II, P for Ves was 0.0039 and P for Tfn was 0.0039); for AP-2 plus dynamin II, P for Ves was 0.0039 and P for Tfn was 0.0039). Ves, vesicles; Tfn, transferrin. (B) Western blot analysis to measure knockdown efficiency in AGS cells. Knockdown efficiency was as follows: for AP-2 (AP2M1) (m2 subunit), 81%; for dynamin II (DNM2), 84%; for AP-2 (m2 subunit) plus dynamin II, 89% and 91%. Tubulin or aldolase was used as the loading control to correlate the amount of protein in each sample.
