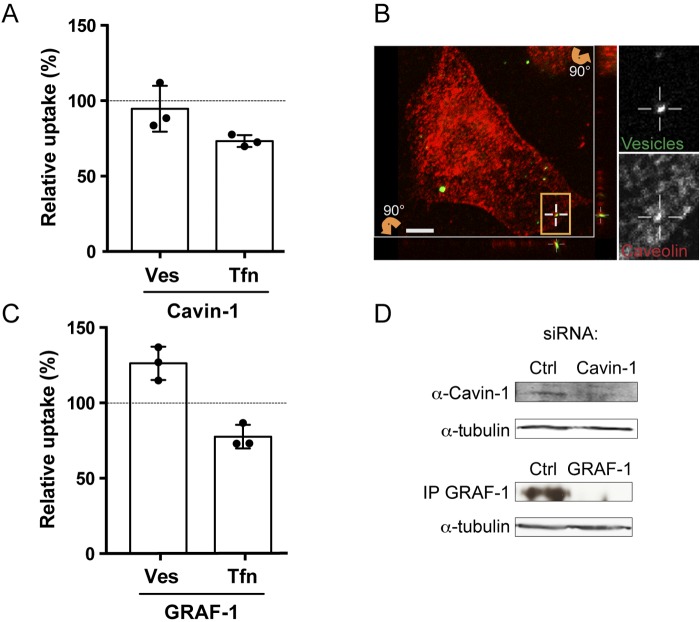
FIG 6 .
Caveolae and CLICs in H. pylori vesicle internalization. (A) H. pylori vesicles were incubated with siRNA-transfected AGS cells for 20 min. In comparison to vesicle uptake in AGS cells transfected with negative siRNA (100%), vesicle internalization was reduced 95% upon cavin-1 knockdown. In comparison to Tfn uptake in AGS cells transfected with negative siRNA (100%), Tfn internalization was reduced to 73% by cavin-1 knockdown. All experiments were performed in triplicate (n = 3). Statistical significance was as follows: for cavin-1, Ves values were NS and P for Tfn was 0.0039. (B) Sections of 3D confocal fluorescent images show colocalization of H. pylori vesicles with caveolin-1 after 30 min. Vesicles were visualized with Strp-FITC (green), and anti-caveolin-1 was detected with secondary Alexa antibodies (red). The boxed regions with colocalizing H. pylori vesicles are enlarged and visualized separately for the green and red channels. Vertical (z) optical sections (x-z and y-z planes) are shown at the bottom and to the right of the large image. Scale bar = 5 µm. (C) H. pylori vesicles were incubated with siRNA-transfected AGS cells for 20 min. In comparison to vesicle uptake in AGS cells transfected with negative siRNA (100%), vesicle internalization was increased to 126% by GRAF-1 knockdown. In comparison to Tfn uptake in AGS cells transfected with negative siRNA (100%), Tfn internalization was reduced to 78% by GRAF-1 knockdown. All experiments were performed in triplicate (n = 3). Statistical significance was as follows: with GRAF-1, P for Ves was 0.0039 and P for Tfn was 0.0039). Ves, vesicles; Tfn, transferrin. (D) Western blot analysis showing a 39% knockdown efficiency of cavin-1 in AGS cells. GRAF-1 knockdown was confirmed by immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. Tubulin was used as the loading control to correlate the protein amount from each sample.