Fig. (2).
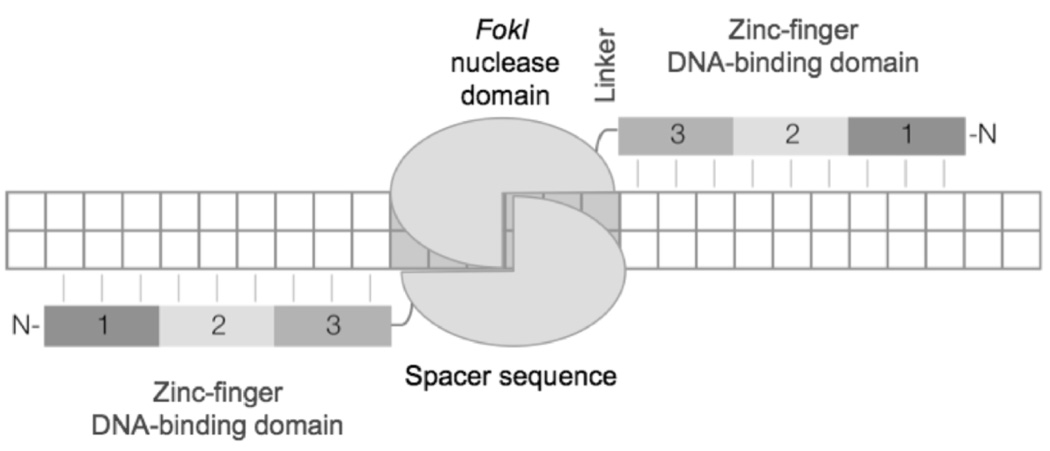
Zinc finger nuclease (ZFN)-mediated DNA double-strand break. A ZFN designed to create a DNA double-strand break (DSB) in the target consists of two monomers. Each monomer encompasses three zinc-fingers (1, 2, 3), which recognize 9 base pairs within the target and a FokI nuclease domain. A short “linker” sequence connects the two domains. The FokI nuclease only functions as a dimer and therefore, following dimerization the nuclease is activated and cleaves the DNA within the spacer sequence.