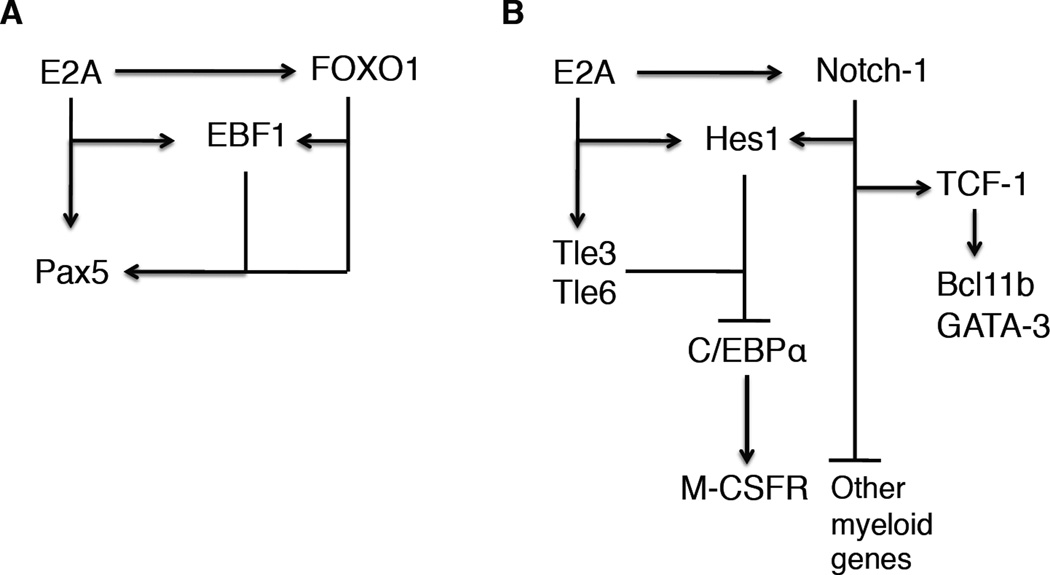
Figure 2. Regulatory networks that orchestrate B and T cell fate.
A Transcription factors that promote early B cell development are indicated. EBF1 functions as a nodal point. Note that E2A acts to induce the expression of FOXO1. E2A and FOXO1 then act collaboratively to activate EBF1 expression. Arrows refer to positive regulation. Bars refer to transcriptional repression. B Transcription factors that promote early T cell development. Notch signaling and E2A, together with Tle3 and Tle6, drive Hes1 transcription, which in turn acts to suppress C/EBPα expression. Notch-mediated signaling leads to the activation of TCF-1, GATA-3 and Bcl11b expression.