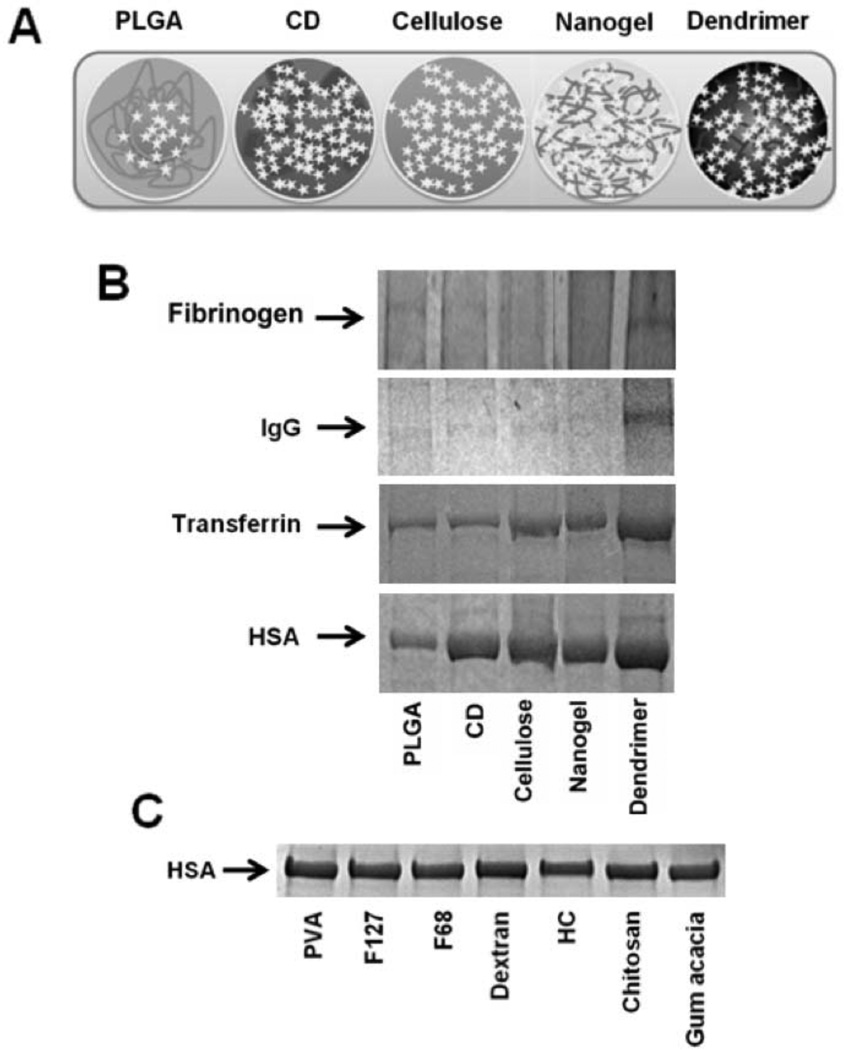
Fig. (4).
Influence of plasma proteins interaction with curcumin nanoformulations. (A) Structurally varied curcumin nanoformulations generated by different methods. Curcumin nanoformulations (20 µM) were incubated in 100 µg human plasma proteins and after 2 hours of incubation, adsorbed proteins were separated by ultra centrifugation and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was run at 150 V for 60 minutes and resultant stained with Coomassie® G-250 stain. (B) Fibrinogen, immunoglobulin G (IgG), transferrin, and serum albumin bound to curcumin nanoformulations. (C) HSA associated with PLGA nanoformulations which are prepared in the presence of various stabilizers. CD: β-cyclodextrin; CUR: curcumin; PLGA: poly(lactide-co-glycolide); Nanogel: poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide); Dendrimer: polyaminoamide (4 generation) based curcumin NPs. F127 and F68 are Pluronic polymers and HC indicates hydroxy cellulose. Figure 3A–B has been reprinted with permission from Dove Medical Press (Copyright Clearance Center, Order License No: 3059490805921) See Ref. 73.