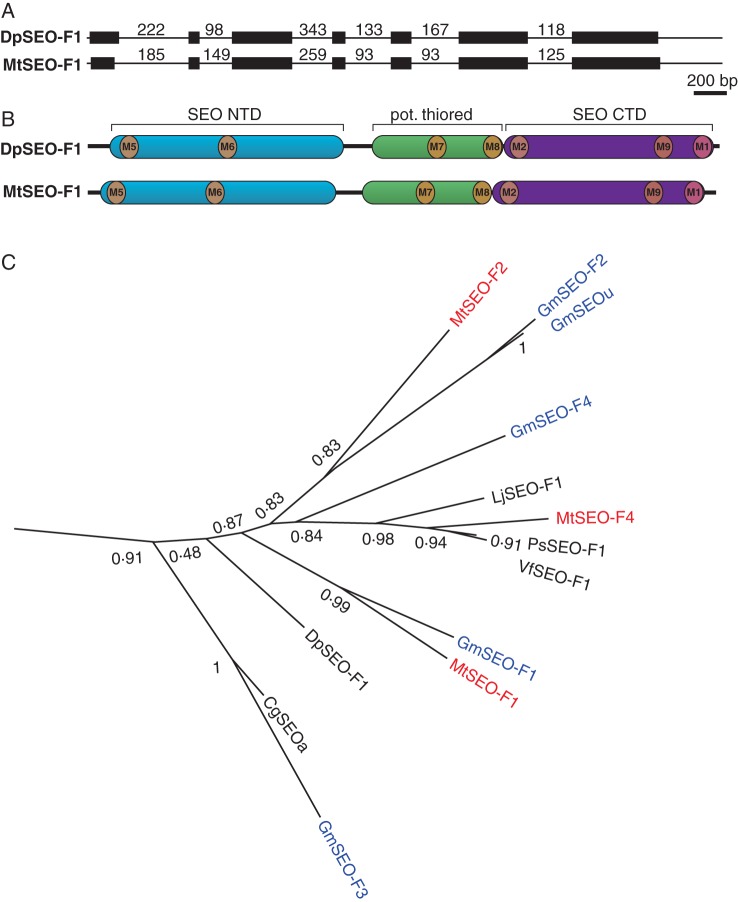
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of group 1 SEO proteins. (A) Genomic organization of DpSEO-F1 compared with the common organization of SEO genes, represented by MtSEO-F1. Exons are represented by black boxes and introns by black lines (not to scale, but the length of each intron is indicated in base pairs). (B) Schematic representation of SEO protein domain organization. DpSEO-F1 comprises an N-terminal domain (SEO NTD; blue), a potential thioredoxin fold (pot. thiored, green) and a C-terminal domain (SEO CTD; purple). This specific combination is only present in SEO proteins (Rüping et al., 2010). The positions of previously described motifs (M1, M2; Rüping et al., 2010) and newly identified motifs (M5–M9; Supplementary Data Fig. S2) are indicated. (C) Group 1 of the phylogram created with FastTree2 based on MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004) amino acid alignment (Supplementary Data Fig. S1). SEO proteins previously described by Rüping et al. (2010) as well as DpSEO-F1 and LjSEO-F1 were used to construct the phylogram. The number of amino acid substitutions is related to branch length, and bootstrap values are indicated.