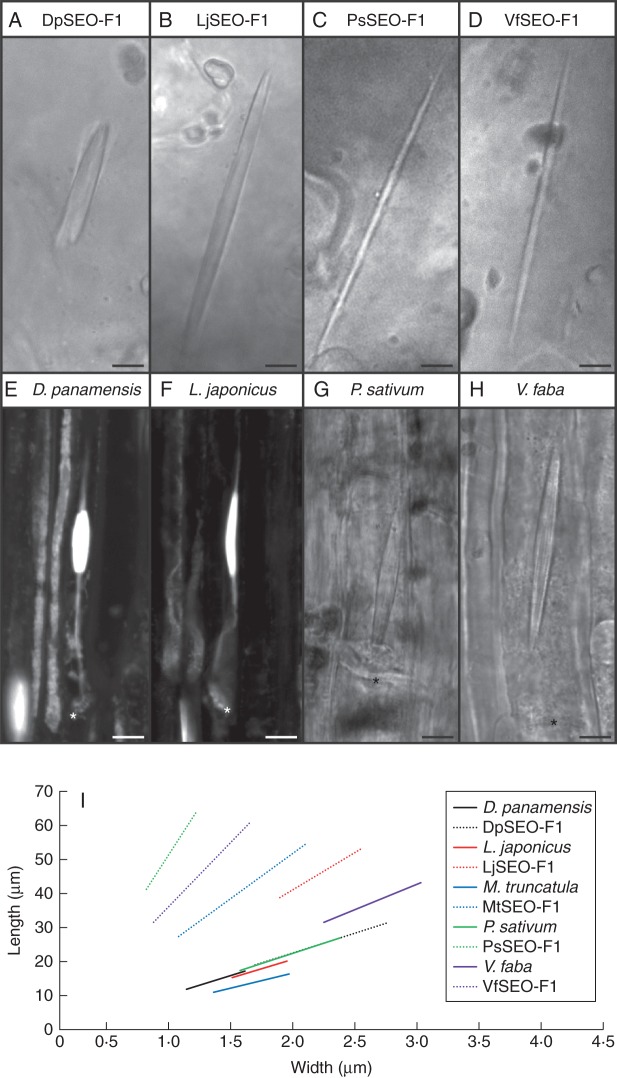
Fig. 3.
Morphology of artificial forisomes compared with native forisomes. Artificial forisomes were produced by heterologous expression in N. benthamiana epidermal cells. (A) DpSEO-F1 expression produced short, wide protein bodies. (B) LjSEO-F1 expression produced homomeric forisome-like protein bodies with the typical spindle shape. (C, D) The expression of PsSEO-F1 (C) and VfSEO-F1 (D) produced long, thin protein bodies. (E, F) Native forisomes of D. panamensis (E) and L. japonicus (F) in sieve elements. Sieve plates are marked with an asterisk. Forisomes were stained with sulphorhodamine 101 to visualize the tails. (G, H) Native P. sativum (G) and V. faba (H) forisomes in sieve elements. Sieve plates are marked with an asterisk. (I) Schematic overview summarizing the proportions of artificial and native forisomes (mean length, mean width and mean ratio). The range of the graphs is adjusted to the standard deviations of length and width. Artificial forisomes are represented by dotted lines and corresponding native forisomes are shown by solid lines in the same colour. Scale bars: (A–H) = 5 μm.