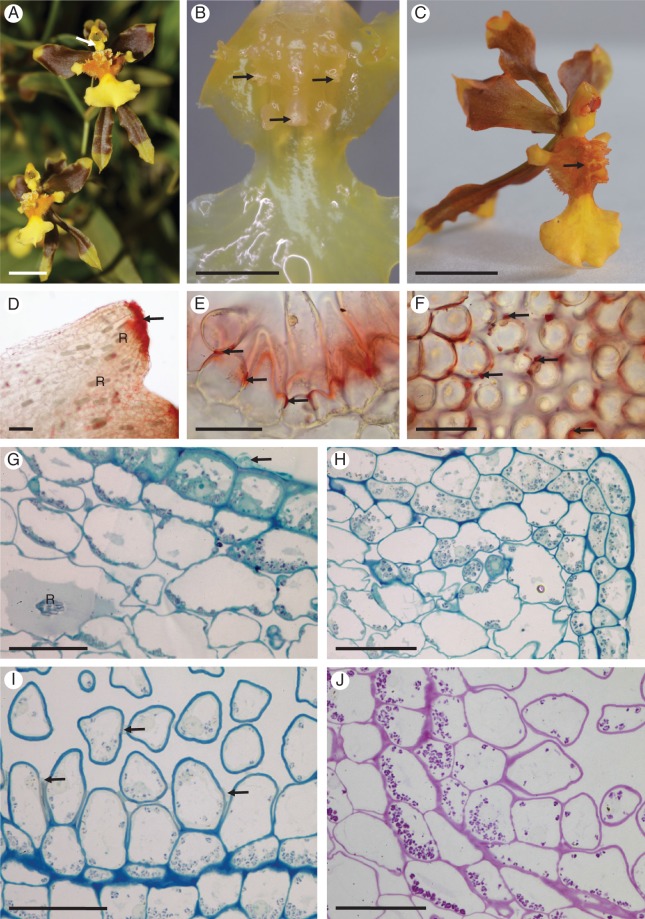
Fig. 1.
Gomesa longipes: habit and LM. (A) Habit of flower with pronounced callus and tabula infrastigmatica (arrow). (B) Callus showing projections (arrows). (C) Entire flower following immersion in alcoholic Sudan III solution clearly showing stained callus region (arrow). Note the pronounced tabula infrastigmatica. (D) Apical part of callus projection stains red for lipids (arrow) following treatment with Sudan III. Numerous idioblasts containing raphides occur in the ground parenchyma. (E) Lipid-rich material is also present towards the bases of trichomes (arrows). (F) Lipid droplets also occur on the surface of epidermal papillae (arrows). (G) Section of callus stained with MB/AII showing glabrous epidermis and residues of secreted material (arrow) on the callus surface. (H) Section of callus projection stained with MB/AII. Epidermal and ground parenchyma cells contain amyloplasts. (I, J) Section of callus epidermis with trichomes. Note the thick tangential cell walls of sub-epidermal parenchyma. (I) Secretory residues (arrows) following staining with MB/AII. (J) Starch grains within trichomatous and atrichomatous epidermal cells, together with ground parenchyma cells, following the PAS reaction. Scale bars = 1 cm, 3 mm, 1 cm, 100 μm, 50 μm, 50 μm, 50 μm, 50 μm, 50 μm, 50 μm, respectively. R, idioblasts with raphides.