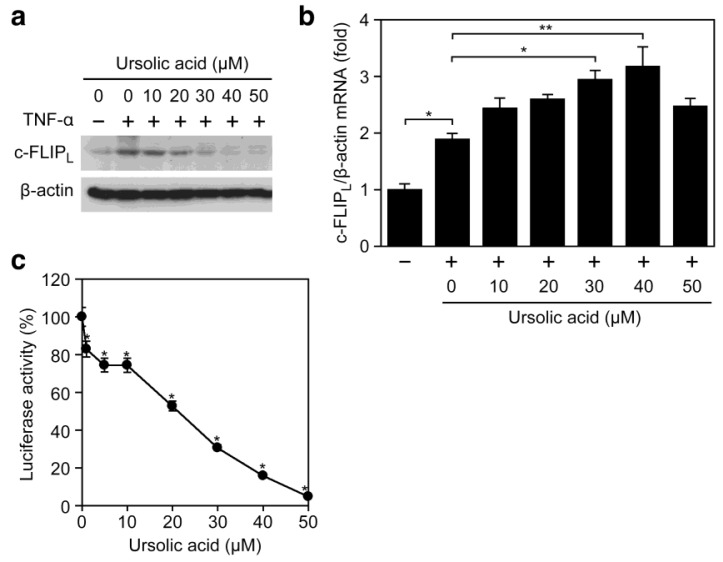
Figure 4.
Ursolic acid inhibits TNF-α-induced expression of NF-κB-responsive genes. (a) A549 cells were preincubated with various concentrations of ursolic acid for 1 h and then incubated with (+) or without (–) TNF-α (2.5 ng/mL) for 6 h in the presence or absence of ursolic acid. Protein expression of c-FLIPL was analyzed by Western blotting; (b) A549 cells were pretreated with indicated concentrations of ursolic acid for 1 h and then incubated with (+) or without (–) TNF-α (2.5 ng/mL) for 6 h in the presence of ursolic acid. c-FLIPL mRNA expression was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. The ratio of c-FLIPL mRNA relative to β-actin mRNA is shown as means ± SD (n = 3). * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01, compared with control; (c) A549 cells were transiently transfected with the NF-κB-responsive luciferase reporter for 24 h. The cells were preincubated with various concentrations of ursolic acid for 1 h and then incubated with TNF-α (2.5 ng/mL) for 6 h in the presence of ursolic acid. Cell lysates were prepared and their luciferase activities measured. Luciferase activity (%) is shown as means ± SD (n = 3). * P < 0.01, compared with control.