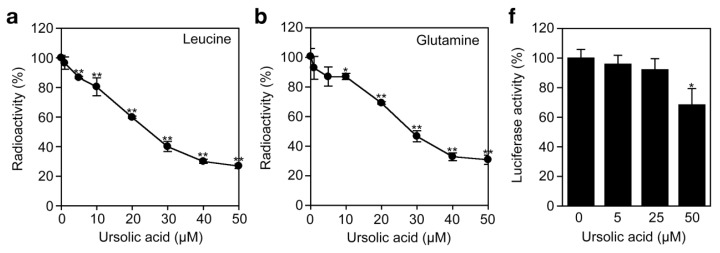
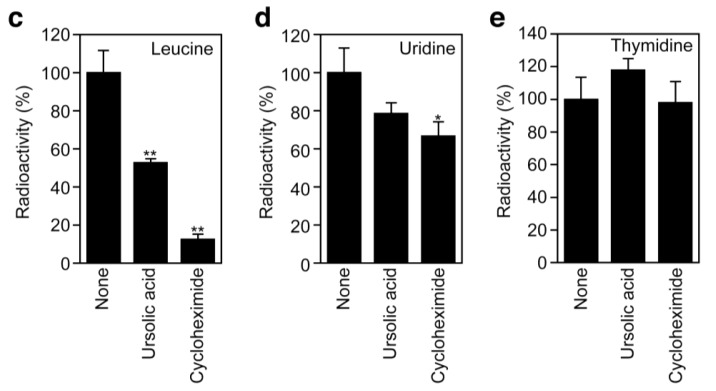
Figure 6.
Ursolic acid inhibits cellular protein synthesis. (a and b) A549 cells were incubated with various concentrations of ursolic acid for 5 h and then incubated with [3H]L-leucine (a) or [3H]L-glutamine (b) for 2 h in the presence of ursolic acid. Radioactivity incorporated into the acid-insoluble fractions was measured. Radioactivity (%) is shown as means ± SD (n = 3). * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01, compared with control; (c to e) A549 cells were preincubated with or without ursolic acid (50 μM) or cycloheximide (10 μM) for 1 h and then incubated with [3H]L-leucine (c), [3H]uridine (d), or [3H]thymidine (e) for 2 h in the presence or absence of those compounds. Radioactivity incorporated into the acid-insoluble fractions was measured. Radioactivity (%) is shown as means ± SD (n = 3). * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01, compared with control; (f) Luciferase mRNA was translated by rabbit reticulocyte lysates in the presence of indicated concentrations of ursolic acid at 30 °C for 90 min. Luciferase activity (%) is shown as means ± SD (n = 3). * P < 0.01, compared with control.