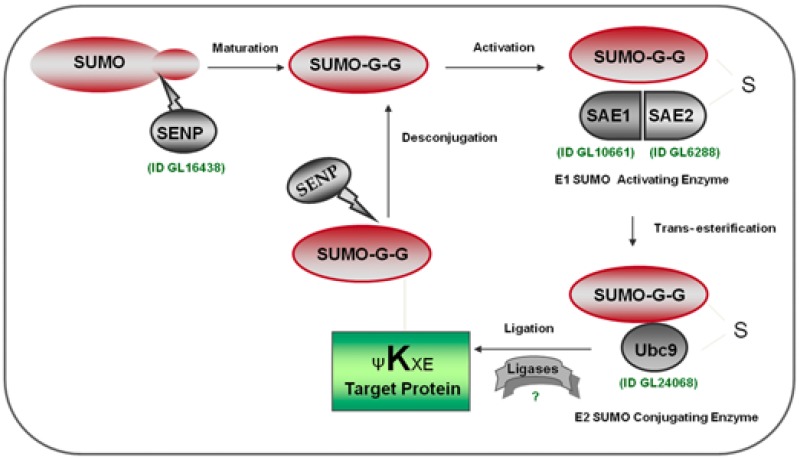
Figure 1.
The SUMO conjugation pathway. SUMO is expressed as an inactive propeptide and is processed by a SUMO-specific protease (SENP) to expose the C-terminal GG, required by the SUMO conjugation to targets (maturation). Mature SUMO is activated by the SUMO activating enzyme (E1) and is transferred through a transesterification process to Ubc9 (E2). SUMO is next conjugated to the target lysine of a substrate, defined by the consensus motif ΨKXE. E3 ligase enzyme can facilitate this process. Specific proteases can remove SUMO from modified substrates maintaining the reserve of free SUMO. Gene ID corresponding to homologous Giardia enzymes involve in the SUMOylation process is depicted in green. Modified from [10].