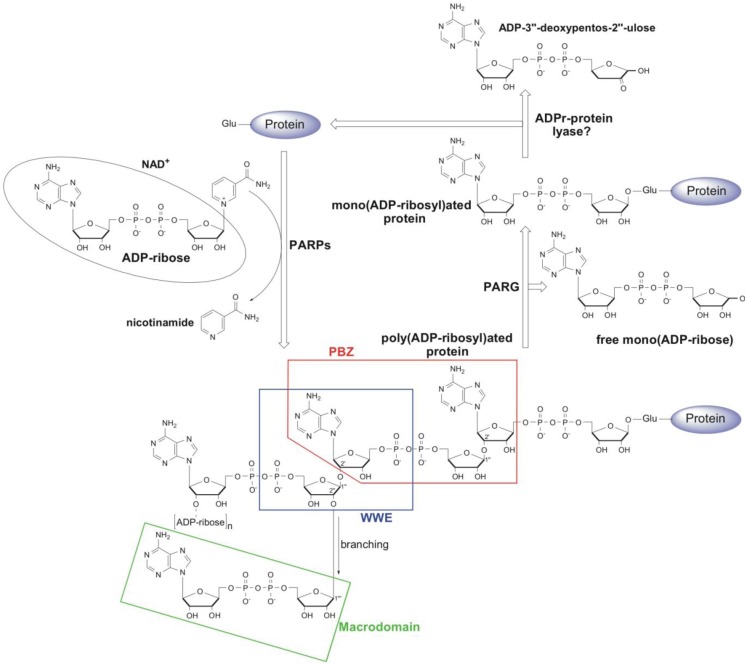
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation (PAR) metabolism. PARPs catalyse the transfer of an ADP-ribose moiety from NAD+ to a target protein with the concomitant release of nicotinamide. The first ADP-ribose is attached via an ester linkage to the glutamate on the target protein. The subsequent transfer of additional ADP-ribose molecules through the 2',1''- and 2'',1'''-O-glycosidic bond leads to the synthesis of linear and branched PAR polymers, respectively. PARG cleaves PAR chains and releases mono(ADP-ribose), whilst the proximal ADP-ribose is removed by ADP-ribosyl protein lyase. Regions of PAR recognised by Poly(ADP-Ribose)-Binding Zinc Finger (PBZ), WWE and macrodomain PAR-binding modules are boxed.