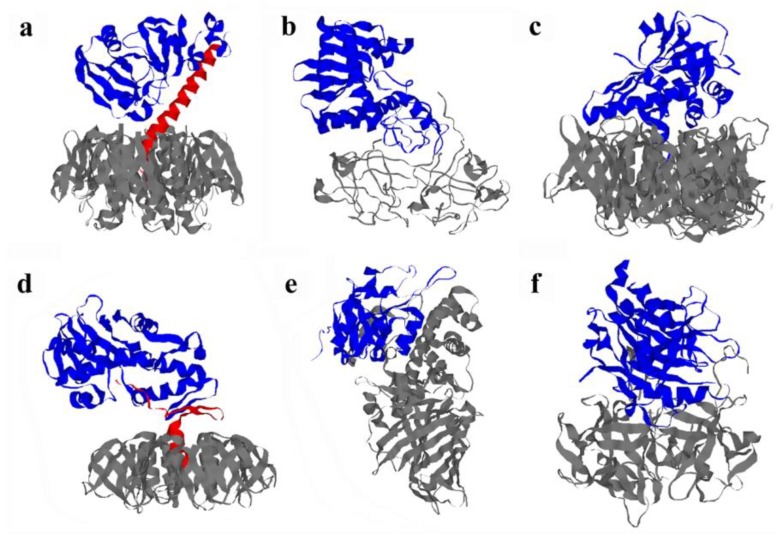
Figure 2.
Structural organization of AB-type, ER-translocating toxins. (a) Ribbon diagram of cholera toxin (Ctx; PDB 1S5F, [33]). The A1 subunit is in blue; the A2 linker is red; and the B homopentamer is grey. The CtxB pentamer recognizes GM1 gangliosides on the host cell surface, while CtxA1 is an ADP-ribosyltransferase that elevates intracellular cAMP levels by activating the stimulatory α subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein; (b) Ribbon diagram of ricin toxin (Rtx; PDB 2AAI, [34]). RtxA is in blue, and RtxB is in grey. RtxB binds to a wide range of glycoproteins and glycolipids with terminal galactose residues, while RtxA is an N-glycosidase that inhibits protein synthesis by removing a specific adenine residue from the 28S rRNA; (c) Ribbon diagram of pertussis toxin (Ptx; PDB 1PRT, [35]). The catalytic S1 subunit is in blue, and the five subunits of the B pentamer (S2, S3, two copies of S4, and S5) are grey. PtxB can bind to a variety of glycoconjugates, while PtxS1 is an ADP-ribosyltransferase that elevates intracellular cAMP levels by locking the inhibitory α subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein in an inactive state; (d) Ribbon diagram of Shiga toxin (Stx; PDB 1DM0, [36]). The A1 subunit is in blue; the A2 linker is in red; and the B homopentamer is grey. The StxB pentamer binds to globoside Gb3 on the host cell surface, while StxA1 is an N-glycosidase that inhibits protein synthesis by removing a specific adenine residue from the 28S rRNA. The Stx family includes Stx from Shigella dysenteriae (pictured) and the Shiga-like toxins (Stx1, Stx2, and Stx2 isoforms) from Escherichia coli; (e) Ribbon diagram of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A (EtxA; PDB 1IKQ, [37]). The catalytic moiety (domain III) is in blue, and the B moiety (domains I and II) is in grey. The B moiety of EtxA binds to the α-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein on the host plasma membrane, while the A moiety of EtxA is an ADP-ribosyltransferase that inhibits protein synthesis through the modification of elongation factor 2; (f) Ribbon diagram of cytolethal distending toxin (Cdtx; PDB 1SR4, [38]). The catalytic CdtxB subunit is in blue, while the cell-binding CdtxA and CdtxC subunits are in grey. The cell-binding heterodimer binds to cholesterol and glycoconjugates, while the CdtxB subunit is a type I DNase that induces cell cycle arrest by causing double-stranded DNA breaks.