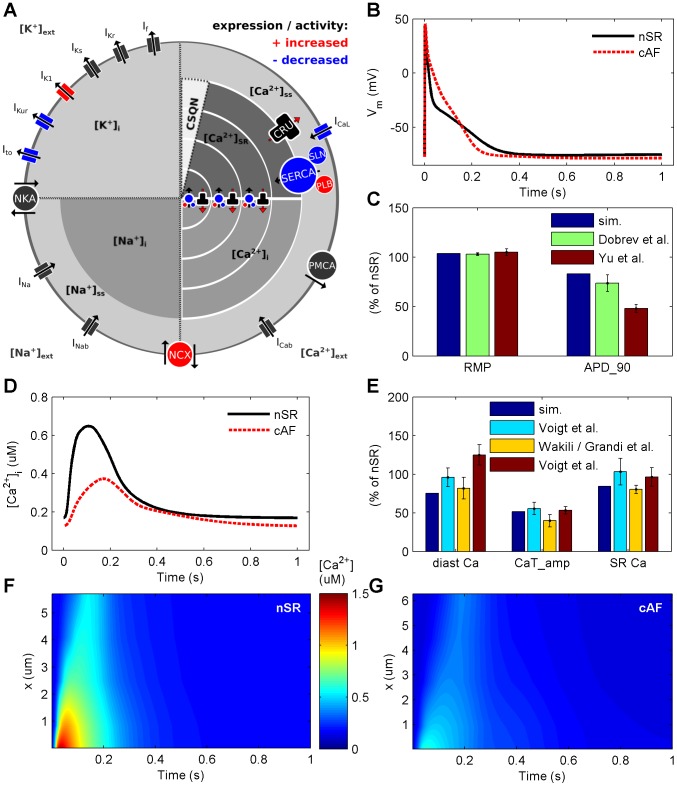
Figure 1. Illustration of cAF-remodeling processes accounted for in the model and consequent changes in electrophysiological properties and Ca2+ dynamics.
(A) Schematic presentation of the cell model. Ionic currents and ion concentrations are referred to with IX and [Xz]compartment, respectively. Furthermore, NKA = sodium potassium ATPase, NCX = sodium Ca2+ exchanger, PMCA = plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase, SERCA = sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase, PLB = phospholamban, SLN = sarcolipin and CRU = calcium release unit or ryanodine receptor. Colour coding with red and blue refers to increased and decreased activity and/or expression of cellular components (proteins involved in ion transport), respectively. (B & C) cAF-remodeling shortens the AP and hyperpolarizes the membrane. Simulation results are compared to in vitro findings of Yu et al. [42] and Dobrev et al. [43]. (D & E) cAF-remodeling decreases the amplitude of CaT, diastolic Ca2+ concentration and SR Ca2+ content, corresponding to in vitro results of Voigt et al. [21] (cyan bar), Voigt et al. [14] (red bar), Wakili et al. [10] (diastolic Ca2+) and Grandi et al. [11] (CaTamp and SR Ca2+ content). (F & G) Spatiotemporal view of the CaT along the radial direction of the virtual cell in nSR and cAF (x = distance from sarcolemma).