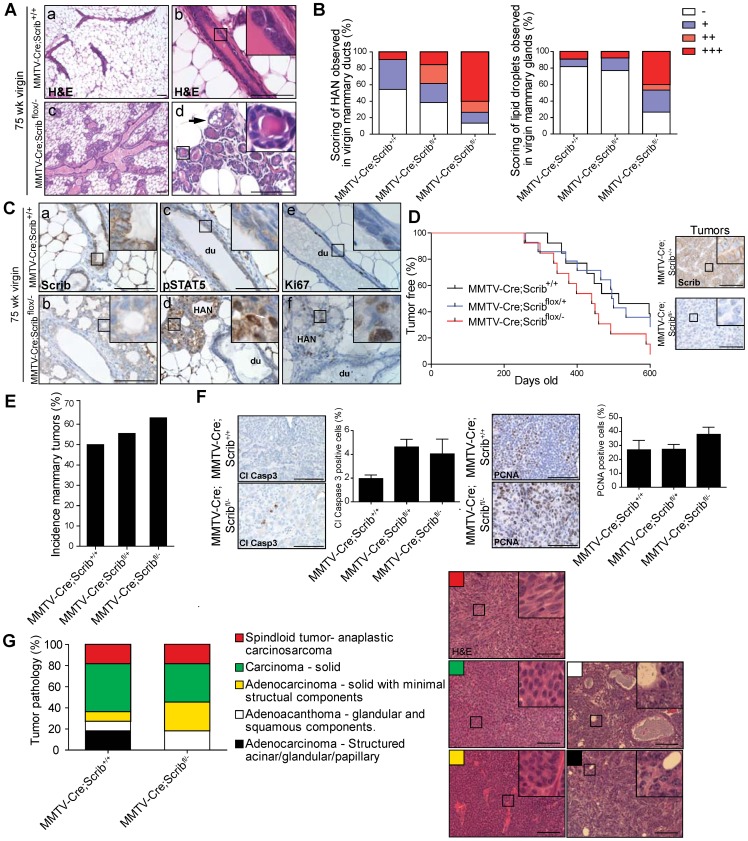
Figure 6. Scribble loss enhances mammary tumourigenesis.
A. Histological analysis of ductal architecture in 75 week mice by H&E staining show hyperplastic alveolar nodules (HAN) in MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/− mice (c, d) compared to control (a, b) as indicated by appearance of circular lobules and lipid droplets (d, black arrow). B. Quantitation of rare (<20%, +), frequent (20–80%, ++), or extensive (>80%, +++) observable alveolar or lipid droplets within mammary epithelium. C. IHC of Scribble (a, b), pSTAT5 (c, d) and Ki67 (e, f) in mammary ducts (du) or HAN of 75 week MMTV-Cre control or MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/− mice. Scale bar = 100 µm. D. Tumour-free plot for MMTV-Cre (n = 19), MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/+ (n = 20) and MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/− (n = 19) virgin mice palpated weekly for mammary tumours. Scribble loss detected by IHC in tumours from MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/− aged mice. Scale bar = 100 µm. E. Incidence of mammary tumours amongst cohorts of MMTV-Cre, MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/+ and MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/− 525 day old virgin mice. F. Tumours from MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/− aged mice show increased cell turnover rates as quantified by PCNA and Cleaved caspase 3 IHC. Scale bar = 100 µm. G. Comparative tumour pathologies show tumours from MMTV-Cre;Scribflox/− aged mice (n = 11) are more progressed and lack structural acinar/glandular characteristics compared to tumours from MMTV-Cre mice (n = 11). Representative H&E staining of tumour classifications. Scale bar = 100 µm. see also Figure S6.