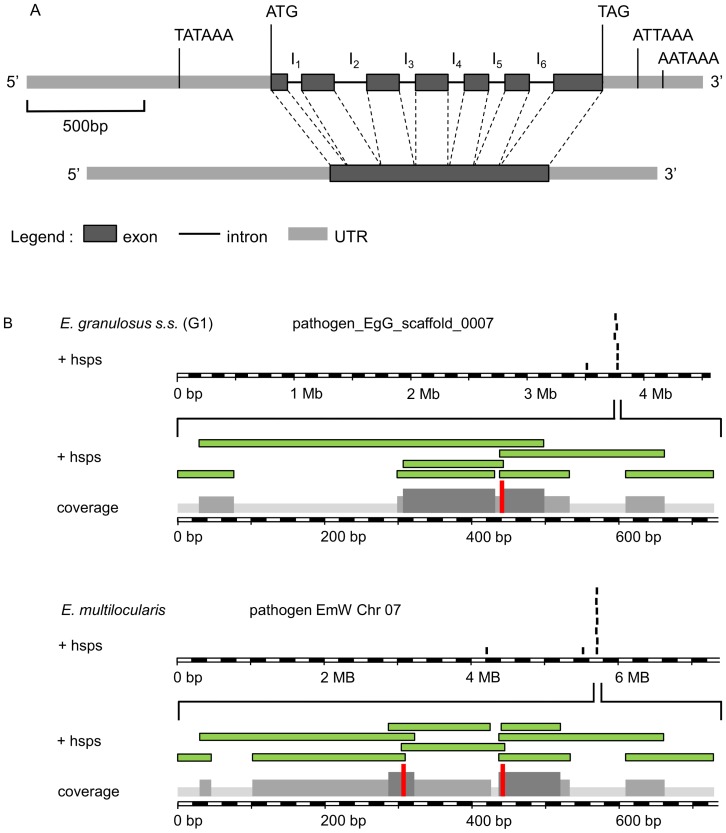
Figure 1. Determination of copy number and molecular structure of the Echinococcus p29 gene.
(A) Exon/intron structure analysis of the Echinococcus p29 gene mapped to the alignments of full-length cDNA with the genomic DNA. The p29 gene is of 1200 base pairs from the ATG start codon at position +1 to the TAG stop codon at positon +1200 and consists of 7 exons separated by six introns. At position P (−552) upstream of the start codon, we identified a TATA box and a eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory element. Additionally two possible polyadenylation sites were identified downstream of the TAG codon on P (+1365) and P (+1510) positions. (B) Graphical output of the BLAST analysis of p29 cDNA (GenBank, accession no. AF078931) beween E. granulosus s.s. (G1) and E. multilocularis genomes performed at the Echinococcus blast server (available at: (available at: http://www.sanger.ac.uk/cgi-bin/blast/submitblast/Echinococcus). The diagram shows the reads with significant BLAST scores to p29 cDNA query (+hsps; high score probability). The reads cluster belongs to the same contig; pathogen_EgG_scaffold_0007 and pathogen EmW Chr 07 for E. granulosus and E. multilocualris respectively. Reads from the same cluster are contiguous and overlapping DNA fragments and when assembled resulted in a single and complete p29 gene sequence.