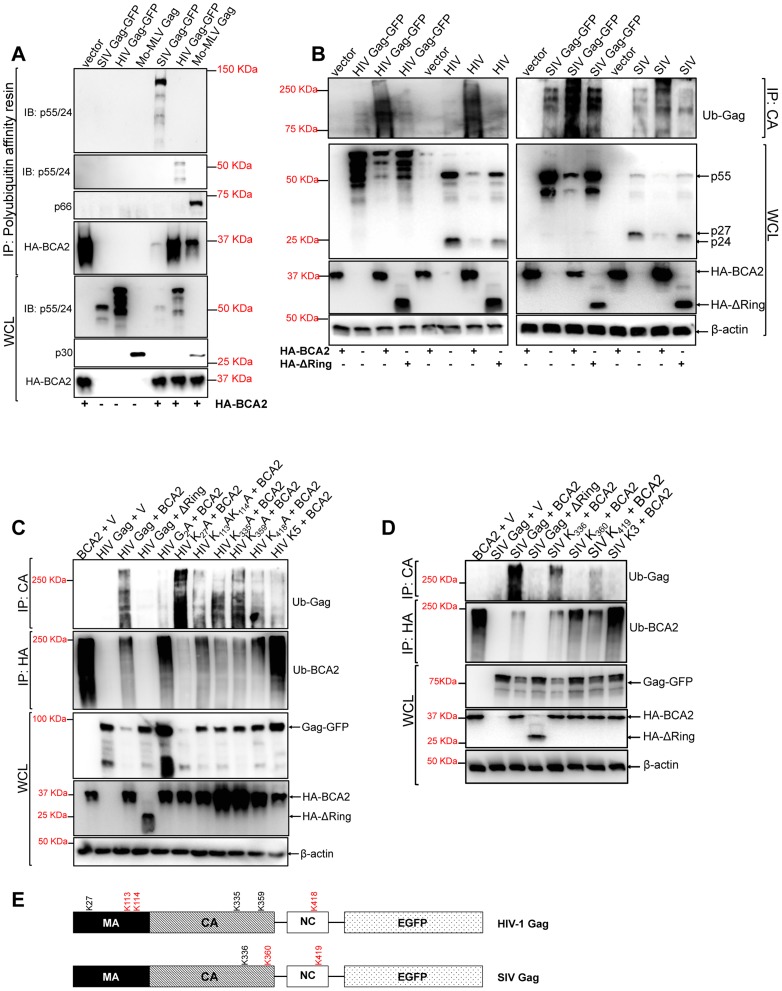
Figure 3. BCA2 induces the ubiquitination of retroviral Gag proteins.
Retroviral Gag proteins were tested for BCA2-induced ubiquitination by co-transfecting 293T cells with vectors expressing codon-optimized HIV-1 NL4-3, SIVmac239 and Mo-MLV Gag proteins along with an expression vector coding for HA-BCA2 or empty vector. (A) Cell lysates were incubated with a polyubiquitin affinity resin and the bound fraction was eluted and analyzed by western blot. Membranes were probed with antibodies specific for p55/p24, MLV p30 and HA. Whole cell lysates were set aside for western blot analyses. (B) The BCA2-induced ubiquitination of Gag-GFP as well as native Gag was analyzed in side-by-side experiments. 293T cells were co-transfected in duplicate with each Gag construct, HA-BCA2, ΔRing BCA2 or empty vector. Cell lysates were set aside for regular western blotting, and the rest of the lysates were immunoprecipitated with an antibody anti-CA. Membranes were developed with an anti-Ubiquitin (Ub) antibody. (C) The ubiquitination of HIV-1 Gag, or HIV-1 Gag mutants, in cells expressing HA-BCA2 was also analyzed by immunoprecipitation. Cell lysates were set aside for western blot analyses and the rest of the samples were immunoprecipitated with an anti-CA specific antibody. Membranes were probed with an anti-Ubiquitin antibody. Similarly, the ubiquitination levels of HA-BCA2 were also determined. In this case, samples were immunoprecipitated using an anti-HA antibody. Results were confirmed in two additional independent assays. (D) A similar approach was used to analyze the ubiquitination levels of SIV Gag, or SIV Gag mutants, in the presence and absence of HA-BCA2. (E) Schematic representation of the putative lysine residues susceptible to become ubiquitinated by BCA2 in HIV-1 and SIV Gag (red). IP: immunoprecipitation. IB: immunoblot. WCL: whole cell lysate. V: empty vector.