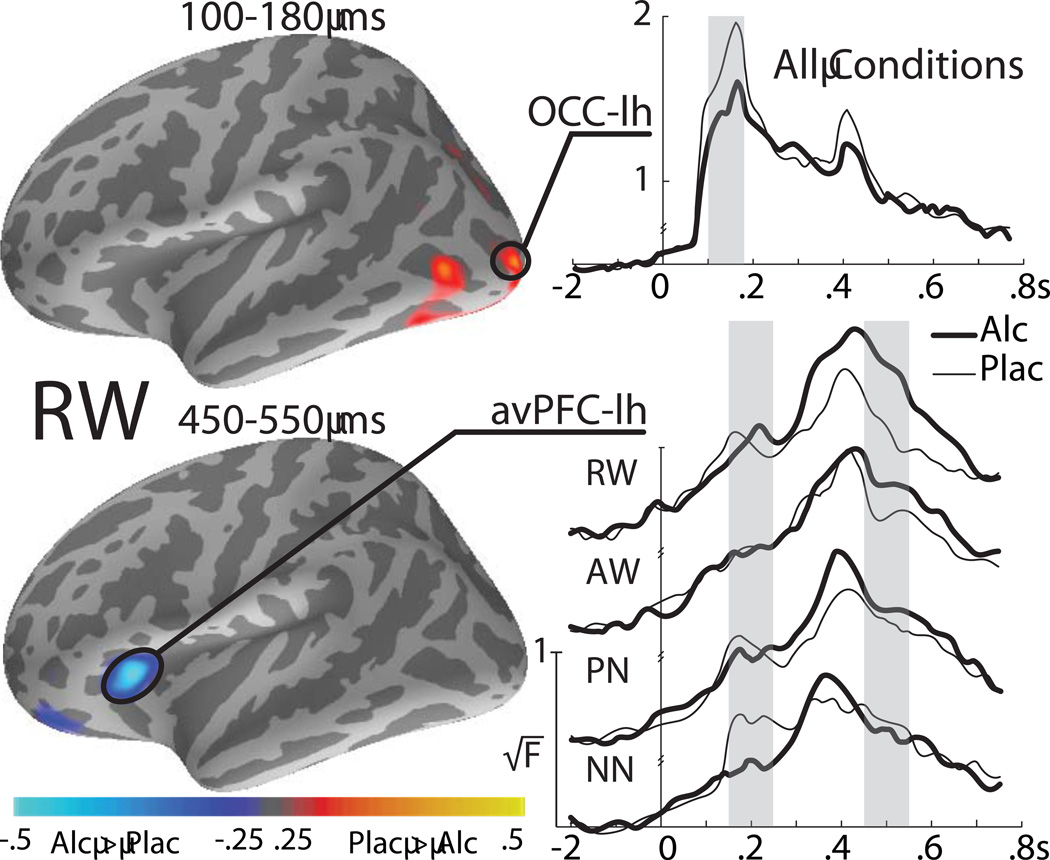
Fig. 5.
Effects of alcohol intoxication on MEG estimates: group average dSPMs of the placebo - alcohol differences (left column) and average time courses of the estimated dipole strength in the left occipital and avPFC ROIs (right panel). Alcohol intoxication attenuates early visual activity overall in the occipitotemporal cortex. In the left avPFC alcohol attenuates activity to NN during an early latency window and it augments later activity to real words. Gray bars denote time windows during which there were significant effects of alcohol on activity estimates. Occ: occipital area; avPFC: anteroventral prefrontal cortex.