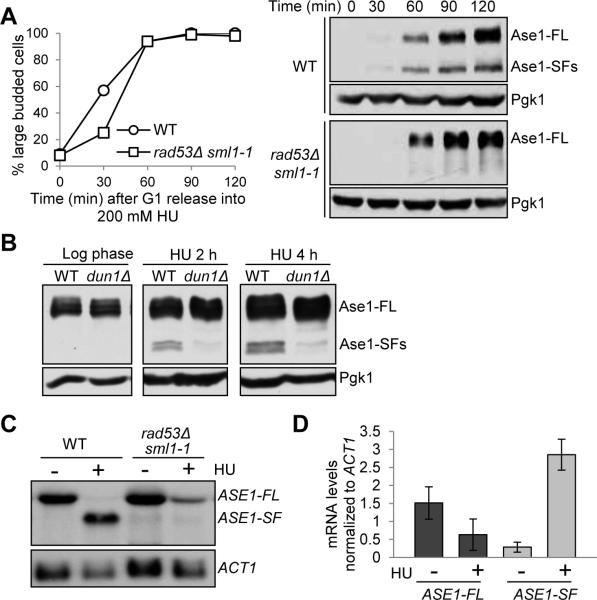
Figure 3. The expression of the Ase1 short isoforms depends on the S-phase checkpoint.
(A) Rad53 is required for Ase1 short protein isoform expression. G1-arrested ASE1-13myc and rad53Δ sml1-1 ASE1-13myc cells were released into YPD containing 200 mM HU. Cells were collected at the indicated time points and protein samples were prepared for western blotting. Budding index was used to indicate cell cycle stage. (B) The expression of Ase1 isoforms in dun1Δ mutants. ASE1-13myc and dun1Δ ASE1-13myc cells were grown to log phase at 30°C and released into YPD containing 200 mM HU. Cells were collected at the indicated time points and protein samples were prepared for western blotting to determine the expression of Ase1 protein. Pgk1 protein levels are shown as a loading control. (C) Intragenic transcription of ASE1 depends on Rad53. G1-arrested WT and rad53Δ sml1-1 cells were released to fresh YPD at 30°C. Twenty min later 200 mM HU was added to half of the cell culture. Cells were harvested 40 min later, washed with 1xPBS and flash frozen with liquid nitrogen. mRNA was prepared and examined by northern blotting with a probe corresponding to nucleotides 2109 to 2411 of the ASE1 gene. ACT1 probe was used for loading control. (D) Quantification of the ASE1 mRNAs in WT cells treated with or without HU from three experiments normalized to ACT1 mRNA using ImageJ software: ASE1-FL –HU (1.51 ± 0.45), ASE1-FL + HU (0.63 ± 0.43), ASE1-SF – HU (0.26 ± 0.14), ASE1-SF + HU (2.86 ± 0.43). See also Figure S3.